Mole Cricket Control: How to Get Rid of the Giant Insect in Your Garden
Content
What kind of insect is this?
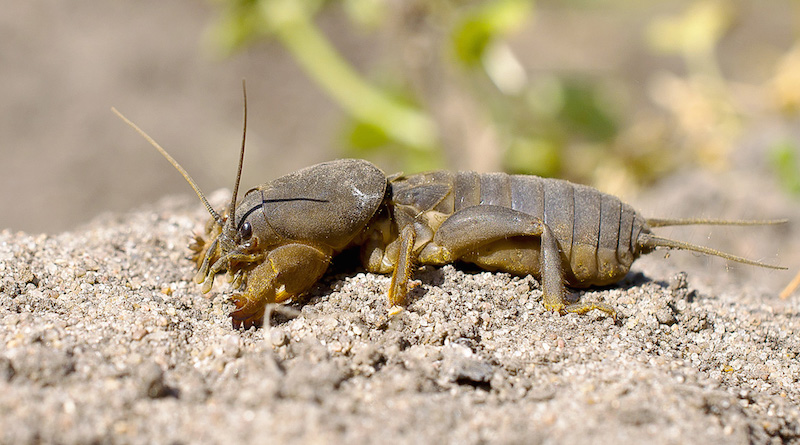
The mole cricket is a large insect belonging to the order Orthoptera. Its body length reaches 6 cm. The pest is covered with a thick shell, which is why it is called the "earth crayfish."
 The head has two large eyes, antennae, and tentacles. The insect digs underground tunnels with its short but powerful front legs. Two appendages are visible at the end of the abdomen.
The head has two large eyes, antennae, and tentacles. The insect digs underground tunnels with its short but powerful front legs. Two appendages are visible at the end of the abdomen.
The pest has elytra and large wings that help it move through the air. The mole cricket can also run fast and swim well, but it spends most of its time underground.
In May and June, females lay eggs in nests they've built. A single clutch can contain up to 500 eggs. The nest is located underground at a depth of at least 10 cm.
Larvae emerge from the eggs after approximately two weeks. They resemble adults, but differ in size and lack wings. The young insects move through underground tunnels, feeding on organic debris. After a year, the young grow to the size of large insects and acquire the ability to dig underground tunnels independently.
The parasite can cover large distances, crawling across a plot or garden, damaging the roots of crops.
What damage does the mole cricket cause in the area?
The parasite damages roots and all underground parts of crops: root collars, tubers, and even seeds. It harms seedlings of various berry and ornamental plants. It most often attacks the following species:
- carrots;
- beets;
- young potatoes;
- cabbage;
- tomatoes;
- radish;
- bell pepper.
The cabbage moth also attacks melons and gourds (watermelons and melons). It feeds on young shoots of hemp and sunflower. Wheat, barley, and rye are also affected by this pest.
In addition to plants, the mole cricket also destroys the larvae of other insects living in the soil, and also feeds on earthworms.
Reasons for the appearance of the mole cricket
 A pest infestation can be detected not only by the eaten crops. As it moves underground, it digs winding tunnels that can be detected by the excavated area.
A pest infestation can be detected not only by the eaten crops. As it moves underground, it digs winding tunnels that can be detected by the excavated area.
The mole cricket requires warmth, so it is comfortable in the southern regions, as well as in the European parts.
The pest doesn't live in northern regions, and arid climates don't suit it. For example, in Siberia, Kazakhstan, and northeastern Russia, gardeners don't even know what this insect looks like.
Ground crickets live on the banks of bodies of water, preferring moist, loose soil. In garden plots, they nest in manure and compost heaps.
Insects appear in gardens thanks to the humus they bring in, which is where they live. They can also crawl over from a neighbor's garden or fly over from a pond.
Signs of appearance
A mole cricket infestation can be detected by several signs. Mounds of earth with tiny holes appear on the ground. They are especially noticeable after rainfall. The insect is active at night. In the morning, an attentive owner will immediately notice traces of its activity.
The presence of the cabbage moth can be determined by the following characteristic factors:
- The appearance of a large number of dried shoots. Sometimes the shoots are gnawed.
- Horizontal passages are visible around the crops, especially after watering.
- The tubers are eaten.
- Round holes have appeared in the beds. These holes serve as entrances to the mole crickets' burrows.
Often, the pests themselves can be found near damaged plants.
Effective ways to get rid of mole crickets

When many gardeners discover insects on their plots, they ask themselves: how to get rid of mole crickets in the garden and vegetable patch.
The choice of pest control depends on the severity of the infestation. If there are numerous pests, insecticides should be used.
Biological treatments are effective, but their effects are long-lasting. Home remedies are suitable for eradicating small populations.
Chemicals
The most effective method of pest control is the use of insecticides. Flavoring and aromatic additives are essential components in the production of these products.
The most common pesticides are:
- "Medvetoks";
- Terradox;
- "Antimerdvedka";
- "Thunder";
- "Rembeck";
- "Prestige".
Before using pesticides, read the instructions and observe the waiting period before harvesting. Sprinkle the pesticides with soil to prevent harm to insects and birds.
Biological agents
Mole crickets can also be controlled on your property using biological agents. Biological agents do not harm the soil or plants. This method is considered gentler and safer.
The following remedies work effectively against pests:
- "Nemabact";
- "Boverin";
- "Metarizine";
- "Biodischarge".
Ultrasound
You can get rid of mole crickets using modern technologies—ultrasonic repellents. These devices emit signals that negatively affect the insects. This discomfort causes them to leave the area.
To scare away the mole cricket, you can use the following devices:
- "Typhoon";
- "Riddex";
- Post Reject.
Folk methods of struggle
If the pest has appeared recently, try to exterminate it using folk remedies, and only then take proactive protective measures.
Homemade traps
The mole cricket can be lured out of its burrows or drawn into any container from which it cannot escape, and then destroyed.
- Attraction by a pleasant smell. Pour a sweet liquid, honey, or beer into a glass jar. Place it at an angle near the burrow.
- Food and shade. Place any porridge (rice or semolina) mixed with sunflower oil into the dug hole. Cover with a piece of roofing felt or thick cardboard. The mole cricket will appear before noon.
- Humus or compost. In the fall, fill the dug holes with manure mixed with straw. Pests will hide there before the cold weather sets in. As soon as the temperature drops to -5 to -8°C, spread the manure over the garden to kill large insects, and the larvae will die in the frost.
Poisoned baits
Soak the grains in a diluted insecticide overnight. Mix the prepared mixture with unrefined sunflower oil. Spread the poisoned product around the garden. The pest dies after eating this.
Unpleasant shower
Pour the prepared liquid into the holes, the insects will crawl out and you can kill them.
Several solution options:
- Laundry soap. Add the crushed soap to a bucket of water. Pour it into each hole.
- Onion peel. Prepare a solution of husks (1 kg) and water (10 l). Let it steep for five days. Pour the infusion into the burrows.
Repelling with smells
Place rags soaked in ammonia or kerosene around the beds.
The mole cricket dislikes such odors. You can also place a small piece of fish in the planting hole.
Repulsive plants
The pest dislikes the smell of herbs and medicinal plants. It's enough to sow marigolds, garlic, calendula, and valerian near the plantings.
Place pine, spruce or fir needles between the potato beds.
Natural enemies of the mole cricket
Hedgehogs, which are active at night, like mole crickets, help to exterminate the insect.
It is necessary to attract useful birds to the site: crows, starlings, rooks, storks.
How to protect seedlings from mole crickets
 Young seedlings suffer the most from pest activity. Even if the bugs don't attack tender shoots, they can still damage fragile roots. Damaged shoots fall over and die.
Young seedlings suffer the most from pest activity. Even if the bugs don't attack tender shoots, they can still damage fragile roots. Damaged shoots fall over and die.
To protect seedlings, the above measures are taken, but individual barriers against mole crickets are a useful and reliable method only for saplings.
The barrier is placed under the soil, surrounding the roots on all sides. Plastic containers, cotton material, and fine-mesh netting can be used for this purpose.
Prevention
To prevent mole crickets from appearing on your property, you must take preventative measures:
- Remove any lying objects (boards, slate) from the area, under which the soil is constantly damp.
- Dishes containing liquid should not leak.
- The brought humus should be loaded into a container and treated with a mole cricket repellent.
- The compost heap must be isolated from contact with the ground.
Periodically, loosen the soil in the area. This will help destroy pest nests, eggs, and ensure deep penetration of various chemicals.
Preventative measures won't protect against a pest infestation if the area is already infested. They can only help prevent accidental infestations brought in with organic matter.