
Methods of grafting fruit trees in spring: choosing the optimal one
Grafting is one of the main methods of growing fruit trees, allowing for high yields and maintaining varietal qualities. In this article, we'll look at the main methods of grafting fruit trees in spring.
Content
What is vaccination?
 Graft – is a method of joining two plants of different varieties. One plant is called the rootstock. It must have a root system and the ability to tolerate adverse conditions. The second plant is called the scion. It must have good fruiting qualities.
Graft – is a method of joining two plants of different varieties. One plant is called the rootstock. It must have a root system and the ability to tolerate adverse conditions. The second plant is called the scion. It must have good fruiting qualities.
Part of one plant is transplanted to another so that they can grow together. The result is a single organism, in which the root system of the mother plant supports the growth and development of the grafted part.
Why is it necessary to graft fruit trees?
Grafting fruit trees produces plants with superior qualities, such as disease resistance, high productivity, and fruit quality. Grafting also helps preserve varietal characteristics.
Selecting material for grafting
For grafting it is necessary to select a rootstock and scion.
Rootstock
 Rootstock – This is the plant that will serve as the base for the graft. The rootstock must be healthy, young, and have a well-developed root system.
Rootstock – This is the plant that will serve as the base for the graft. The rootstock must be healthy, young, and have a well-developed root system.
Scion
 Scion – This is the plant that will be grafted onto the rootstock. The scion must have good fruiting and varietal qualities.
Scion – This is the plant that will be grafted onto the rootstock. The scion must have good fruiting and varietal qualities.
Necessary tools and materials
 The following tools and materials are required for grafting:
The following tools and materials are required for grafting:
- a sharp knife or grafting knife;
- hammer;
- insulating tape;
- garden wax.
Methods of grafting
There are several methods for grafting fruit trees. Let's look at the most common ones.
For the bark

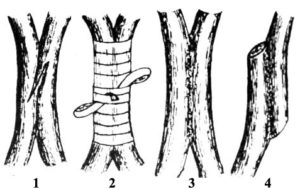
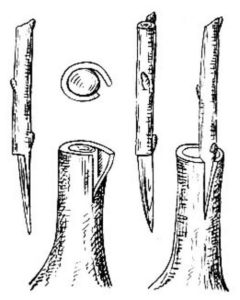 This method of grafting fruit trees involves inserting a scion in the form of a cutting behind the bark of the rootstock. It is necessary to select a healthy one. cutting scion, which has a diameter approximately the same as the diameter of the rootstock branch onto which you are going to graft. The scion stalk must be prepared: a bevel must be made at both ends cutThis will make it easier to insert behind the bark of the rootstock.
This method of grafting fruit trees involves inserting a scion in the form of a cutting behind the bark of the rootstock. It is necessary to select a healthy one. cutting scion, which has a diameter approximately the same as the diameter of the rootstock branch onto which you are going to graft. The scion stalk must be prepared: a bevel must be made at both ends cutThis will make it easier to insert behind the bark of the rootstock.
Before inserting the scion, make a vertical cut approximately 3–5 cm long and 1–1.5 cm deep on the rootstock branch. Then insert the scion into this hole, behind the bark. Wrap the graft site with electrical tape or other material to seal out air and prevent the scion from drying out. Some gardeners also use horticultural wax to seal the graft site.
Absolutely desperate

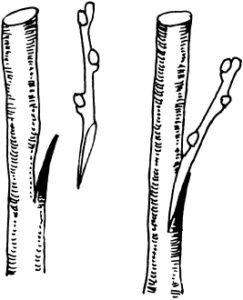 This method of grafting fruit trees involves making matching cuts on the rootstock and scion, after which they are joined. The cuts should be made at a 45-degree angle to the main branch.
This method of grafting fruit trees involves making matching cuts on the rootstock and scion, after which they are joined. The cuts should be made at a 45-degree angle to the main branch.
The cut on the scion should be made in the same place as on the rootstock, but in the opposite direction. After the cuts are made, firmly join the rootstock and scion together. Wrap the graft site with electrical tape or other material.
Into the cleft

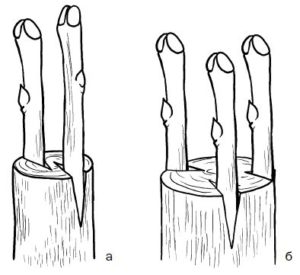 This method of grafting fruit trees is performed using a special tool called a splitter. The rootstock must be free of any damage, ideally new seedlings. The splitter is used to make a T-shaped cut in the rootstock. The scion is then split from below and inserted into the cut.
This method of grafting fruit trees is performed using a special tool called a splitter. The rootstock must be free of any damage, ideally new seedlings. The splitter is used to make a T-shaped cut in the rootstock. The scion is then split from below and inserted into the cut.
After inserting the scion into the cleft The rootstock is wrapped in film or insulating tape to prevent air and dust from entering and to hold the scion in place. After the healing process is complete, the graft site is uncovered.
Copulation

 This is a more complex grafting method, suitable only for experienced gardeners. It involves using a special tool called a copula. It allows the branches of the rootstock and scion to be crossed. The copula should be made on branches of approximately the same diameter. The scion should be prepared and cut to ensure optimal contact between the rootstock and scion.
This is a more complex grafting method, suitable only for experienced gardeners. It involves using a special tool called a copula. It allows the branches of the rootstock and scion to be crossed. The copula should be made on branches of approximately the same diameter. The scion should be prepared and cut to ensure optimal contact between the rootstock and scion.
Once the copula is formed, it is wrapped with special tape to protect it from drying out and other damage. Over time, the tape decomposes, and the scion forms a new shoot on the tree.
Ablation

 This grafting method is used when the tree's top needs to be replaced. The scion must be as fresh as possible to ensure the best possible take.
This grafting method is used when the tree's top needs to be replaced. The scion must be as fresh as possible to ensure the best possible take.
The top of the tree must be removed with a hacksaw so that in place cut All that's left is the trunk. After this, make several cuts on the trunk, 1–2 cm apart. The scion is inserted into the cuts and wrapped with electrical tape to prevent it from drying out.
Budding

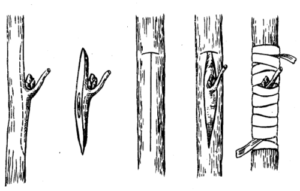 This method of grafting is used for grafting young seedlings and for re-grafting mature trees.
This method of grafting is used for grafting young seedlings and for re-grafting mature trees.
To begin, select young plants with straight stems, approximately 0.5–1.5 cm in diameter, and well-developed buds. The scion should be taken from a healthy plant and approximately 10–15 cm in length.
A T-shaped cut is made on the rootstock, after which a T-shaped piece of bark is removed from the scion. This T-shaped piece easily fits into the cut on the rootstock. Once inserted, the junction is wrapped with tape or film and secured with ribbon.
The scion should be completely immersed in the rootstock, as this promotes rapid fusion and engraftment. If all goes well, the tape can be removed after a few months.
How long does it take for a vaccination to take hold?
The time it takes to take root depends on the grafting method, environmental conditions, and the variety and quality of the material. Generally, it takes from several weeks to several months.
For better engraftment, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the plant and adhere to the regime glaze, take care of the soil and fertilize.
To better understand the grafting process, you can refer to the illustrations that demonstrate how to perform each method. It's important to remember that choosing the right grafting method and using high-quality material will ensure a successful result and promote the development of a healthy and fruitful tree.
Therefore, illustrating spring fruit tree grafting techniques can be an important tool in understanding and mastering this process. This will help you successfully grow fruit trees and reap a bountiful harvest.








