
Apple tree crown formation schemes and branch pruning rules
Forming the apple tree's crown should begin from the moment of planting. Proper pruning accelerates fruiting, increases yield, and improves its quality. Importantly, a properly formed crown is several times more resistant to disease and less susceptible to pest damage.
Content
Basic terms and characteristics
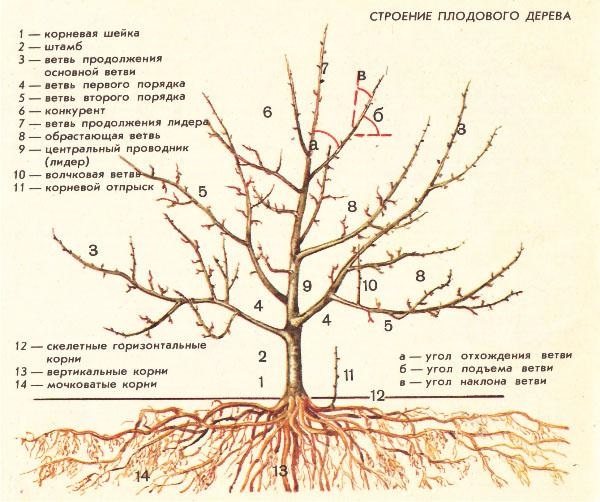
To properly shape an apple tree, you need to know the names and characteristics of the main components of the tree's crown:
- Root collar – the conventional point where the root transitions into the trunk. Located 5–7 cm below the grafting site.
- The trunk is a part of the tree trunk root collar to the first skeletal branch.
- A primary branch, or primary skeletal branch, is a branch that forms the framework (skeleton) of a tree. It extends directly from the trunk and is the thickest and longest. It is not recommended to allow skeletal branches to grow at a right angle to the trunk.
- Second-order branches are fairly large and branch off from first-order branches.
- A competitor is an undesirable, strong, vertical growth shoot growing inward from the crown. It forms after pruning the central conductor and scaffold branches from a bud located below the continuation bud.
- The continuation branch of the leader is formed after cutting off the central conductor from a specially left bud.
- An overgrowing branch is a fourth- and fifth-order branching located on skeletal and second-order branches. They are divided into vegetative (growth) and generative (fruit-bearing) branches.
Vegetative branches ensure tree growth. They also include spring shoots, continuation shoots, replacement shoots, water shoots, and root shoots.
- The central conductor or leader is the section of the trunk from the lower skeletal branch to the base of the leader's branch. It is the main feeder branch for all branches of various orders.
- A water sprout is a strong, growing shoot that grows vertically. It does not bear fruit, but with proper pruning, it can become a secondary branch.
- A root sucker is an adventitious bud that forms on the root system and develops into adventitious shoots. These do not bear fruit and are most often a wild apple species.
- Skeletal horizontal roots are first-order skeletal roots.
- Vertical roots – serve to keep the tree in an upright position.
- Fibrous (adventitious) roots – extend up to 15 m in diameter, supplying the tree with moisture.
A. Angle of departure is the angle at which a branch departs from its supporting branch.
b. The rise angle is the angle between the supporting branch and the branch directed downwards or horizontally.
V. The slope angle is the angle at which a branch bends away from the vertical. It is used to determine the fruiting capacity of branches with a slope of less than 45°.0 from the vertical they grow quickly, but rarely bear fruit, and vice versa.
Reasons for crown formation
A biological characteristic of plants is the desire to reproduce. For this reason, apple trees produce new shoots every year and strive to produce large quantities of fruit. However, such fruits grow small, have an unattractive appearance, and their taste is significantly impaired.

Forming the crown of an apple tree allows:
- prevent the occurrence of bacterial diseases that arise as a result of increased leaf moisture;
- prevent long branches from breaking off, thereby protecting the tree from damage;
- improve the quality of fruits;
- increase crop yields;
- extend the life of an apple tree;
- prevent the death of fruit branches located inside the crown;
- maintain the balance of the branches with fruits, do not allow them to bend or break;
- ensure that sunlight reaches the leader of the tree and the fruits;
- create conditions for harvesting without the use of auxiliary devices.
Lack of pruning for three or more years leads to early aging of the apple tree and a decrease in fruit quality by 50–70%.
Methods of crown formation
To give the apple tree crown the desired shape, the following methods are used:
- Pruning allows you to regulate tree growth. Depending on the timing, it can be:
- winter (spring) – carried out in early spring before the sap begins to flow, but after the threat of recurrent frosts has passed;
- summer – carried out as needed, in case of appearance of unwanted shoots;
- autumn – crown formation after harvesting, but 1 month before the onset of frost.
- Green operation – pinching or removing young and immature shoots.
- Bud blinding (removal) prevents the emergence of unnecessary shoots and conserves nutrients by redirecting them in the right direction. This is the least traumatic method.
- Bending and fixing branches allows you to regulate growth and change the purpose of branches. The desired direction is achieved by hanging weights, installing spacers, or tightening them.
- Grafting is used to fill gaps in the crown.
Basic rules of formation
To form a strong crown, regardless of the method, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules:
- The leader should be higher than all other branches and have the largest diameter.
- All first-order branches should be twice as thin as the leader. Second-order branches should be thinner than the first, and so on. It's important to maintain the principle of subordination of all branches in the crown.
- The angle of inclination of the first order branches should be 45–600. Can be changed by installing a spacer or tie.
- A competitor should not be allowed to grow during the first 3-5 years of a tree's life. An exception might be if the competitor is significantly stronger than the leader's continuation branch; in this case, the competitor's function is transferred to the leader.
As a result of proper formation, air should circulate freely within the crown, and all branches should be well lit by the sun.
Tools and auxiliary materials
 Blinding of buds is done manually, and for pruning you will need the following tools:
Blinding of buds is done manually, and for pruning you will need the following tools:
- A sharp knife. It is preferable for carrying out the procedure, as it is the least traumatic for the tree.
- SecateursUsed to remove long shoots. Causes compression injury to the wood.
- Hacksaw or sawUsed in exceptional cases: for sanitary pruning or to rejuvenate an old tree. It is tissue-damaging.
After removing excess shoots, cuts often appear on branches, often with a rough surface. Wounds up to 1 cm in diameter heal spontaneously. Larger cuts should be treated:
- Garden varnish—a paste made from bee products and natural resin. Contains minerals that promote healing and prevents rot in situ. cut, nourishes the damaged branch.
- White oil paint on natural drying oil – prevents sap leakage and the development of rot.
The processed sections should be observed for a month to prevent the development of rotting processes.
Methods of formation in accordance with the period of apple tree development
Depending on the age of the apple tree, several stages of formation are distinguished.
Formation of a seedling
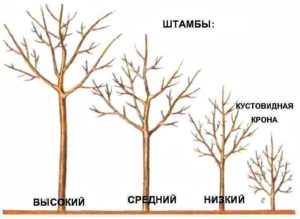 The main task when planting an apple tree in the ground is to form a trunk and create conditions for the development of the root system.
The main task when planting an apple tree in the ground is to form a trunk and create conditions for the development of the root system.
The trunk is the primary connecting link between the roots and the crown of the tree. Its height ranges from 40 to 90 cm. It is the most vulnerable part of the tree, often susceptible to frost or sunburn, which can lead to the death of the entire tree.
There are some differences between pruning a one-year and two-year-old seedling:
- One-year-old seedlings do not have lateral branches, so when planting them, the central leader should be shortened by one-third of its total length. The remaining seedling in the soil should be at least 60 cm tall.
- On two-year-old plants, the leader (as for one-year-olds) and all branches located below 50 cm from the ground should be pruned. From the branches located above, the strongest ones should be selected to form the skeleton, and the rest should be removed. Skeletal branches should be shortened by 2-5 buds.
IN Siberia, on Urals and in the northern regions of Russia it is recommended to leave the trunk no more than 30–50 cm.
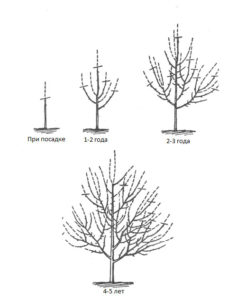
Formation of a young tree
Over the next 5–6 years, the apple tree's crown develops. This process is typically divided into two stages:
- The first three years of life. The main task for three-year-old apple trees is to form skeletal branches with uniform angles in a circle around the leader. Important points:
 mandatory removal of weak shoots, competitors and spinning tops, shortening of skeletal branches;
mandatory removal of weak shoots, competitors and spinning tops, shortening of skeletal branches;- branches of the same tier should be formed at a distance of 15 cm from each other;
- the distance between tiers should be at least 45 cm;
- forming tilt angles by installing spacers or hanging a load to a value of no more than 600;
- Do not allow branches to be positioned directly above each other.
This method of shaping does not delay the apple tree's development. It is recommended to do this in early spring.
- The next 2–3 years. The main goal is to prevent the crown from becoming dense with second-order and subsequent branches. Key points:
- mandatory removal of water sprouts and downward-growing shoots;
- shortening of subordinate branches;
- formation of the angles of inclination of new skeletal branches.
Once the crown has formed, the leader's continuation branch is shortened, leaving a length no less than that of the upper skeletal branches.
Young skeletal branches should be shortened during this period by no more than 2 buds!
Formation of an adult fruit-bearing tree
Formative pruning of a fruit-bearing tree is necessary to regulate growth and create favorable conditions for fruiting.
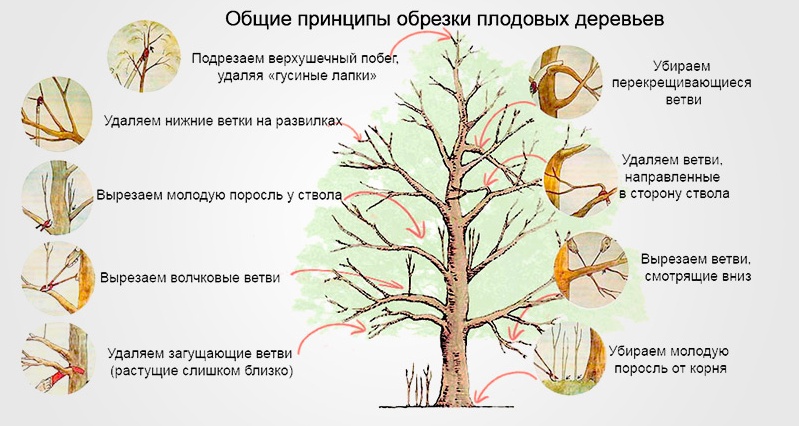
Annual pruning includes:
- Removing suckers from the root. To do this, carefully free the skeletal root from the soil and cut out the sucker with a knife. Cover the removed area with garden pitch and bury the root.
When removing shoots, do not leave stumps, as next year more shoots will grow from them, which will significantly weaken the nutrition of the apple tree.
- Freeing up space within the crown by removing branches:
- broken, damaged or dead;
- nearby growing weaker ones;
- growing downwards or directed towards the trunk;
- crossing (removing the weaker or downward-facing one);
- spinning tops.
When young growth appears in place of a dead skeletal branch, a procedure should be carried out to form a new branch by artificially creating an angle of inclination and securing it.
Formation of an old tree
Old trees should be pruned in the fall, after the leaf fall season begins, but at least one month before the onset of frost. Freezing of unhealed wounds causes bark peeling, which often leads to the death of part of the tree.
Pruning is carried out according to the principle of shaping an adult tree; usually up to 1/3 of the new growth is removed.
Basic apple tree formation schemes
Several factors influence the choice of apple tree formation scheme: planting density, tree age, its structural features, and climatic conditions. After analyzing these factors, one of the most common crown formation schemes should be selected.
Tiered-sparse
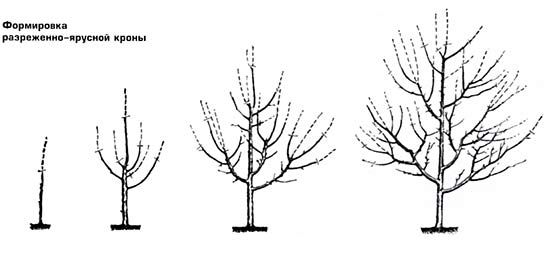
It is carried out in several stages:
- The seedling is cut to a height of 40–80 cm (depending on climate conditions). All lower branches are removed.
- To form the first tier, 3 strong shoots are left.
- The next tier should consist of 5 strong skeletal branches.
- As the tree grows, the distance between tiers should be 50–70 cm.
- On the higher tiers, up to 7 skeletal branches can be formed.
Pruning of competitors, water sprouts and damaged branches should be carried out annually, regardless of the stage of formation of tiers.
After completing the formation, the continuation branch of the leader should be cut to stop growth at a height of 2.5–3.5 m.
The distance between trees should be at least 3–4 m.
Whorled-tiered
One of the simplest crown formation systems.
It consists of two tiers of skeletal branches, spaced 1 m apart. The lower tier contains up to 5 branches, while the upper tier contains no more than 3. The branches of the upper tier are arranged in a staggered pattern above the lower branches.
Vertical palmette

Ideal for small areas and trees growing near walls and fences.
It involves shaping a young seedling on a trellis installed along a fence.
When forming the trunk of an apple tree, two shoots are left at the top and spread out by 900 In relation to each other, a spacer is installed and secured. In subsequent years of growth, the next two branches are left as skeletal branches. The distance between tiers is 60–80 cm.
The height of the tree is regulated by pruning the continuation branch of the leader; annual pruning of excess shoots is carried out according to general rules.
Fusiform
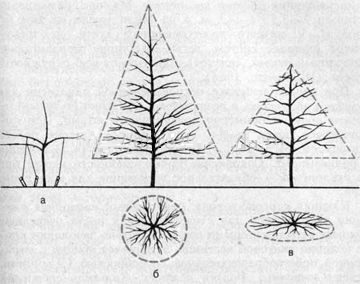
Designed for developing dwarf or dwarf apple tree varieties, this process involves several stages:
- Having measured the desired trunk height, form 3-4 skeletal branches in different directions. Attach weights to them (appropriate for the branches' thickness), and straighten them to a horizontal position (a).
- In the second year, it is necessary to cut off 1/3 of the leader’s continuation branch and continue forming horizontal skeletal branches (b, c).
- Formation continues until the beginning of fruiting (usually 5–6 years).
Peculiarities:
- skeletal branches should be cut back annually by ½, leaving a bud leading outward for the development of subsequent branches;
- The branches located above should be shorter than the lower ones by at least 15 cm.
The height of the tree is regulated by pruning the extension branch of the leader; annual pruning is similar to the general pruning.
Creeping

Ideal for growing apple trees in harsh winter conditions, as well as for forming the crown of dwarf varieties.
The tree seedling is placed in the soil at an angle of 450 southward by grafting the tree onto the ground. At the end of its first summer, the tree is bent down and its skeletal branches are pinned to the ground in a fan shape. In the spring, the clamps are removed, and only new shoots are bent down at the end of summer. Older branches should already have a creeping form.
The tree formed in this way has a height of no more than 50 cm.
The branches of a creeping tree are often attacked by rodents in winter. To prevent this, the snow around the trunk should be firmly packed down.
Bushy
Used for dwarf varieties.
The trunk of such a tree is formed to a height of no more than 40 cm. During the first pruning, 7–8 skeletal branches of the same level are left, and the leader is shortened to 60–70 cm.
Subsequently, shoots are left in different directions with a distance between tiers of no more than 15–20 cm.
It develops over 3–5 years and begins bearing fruit 2 years earlier than usual. Not suitable for varieties with poor branching.
Cup-shaped

Suitable for low-growing varieties.
The lower tier is formed from 3 skeletal branches, spread out at 1200 relative to each other (in the shape of a bowl). The leader is completely cut out, and new shoots are pruned symmetrically at a distance of 40–50 cm from the center.
The disadvantage of this type of shaping is the frequent pruning of internal shoots, which can lead to tree diseases.
Flat crown
To form a flat crown, two skeletal branches must be left and positioned horizontally. All young shoots from the center are removed. The crown of such a tree warms well in the sun, but constant pruning is harmful to the plant.
Sanitary pruning
Sanitary pruning can be performed several times per season. It doesn't involve crown shaping, but rather removes dead or diseased parts of the tree.
It is carried out in the spring and as problems arise using the general technology of pruning and treating cuts.
Features of pruning technology
- Pruning skeletal branches. When forming first-order skeletal bones, long shoots should be shortened to 3–5 buds, making cut Directly above the outward-facing bud, a branch of the next order emerges from this bud, diverging as much as possible from the parent bud.
Weak skeletal branches should be pruned slightly more than strong ones, as this promotes their strengthening and rapid growth.
 Pruning above the outer bud. Carried out at a 45-degree angle.0The lower cut should be level with the underside of the bud, and the upper cut should be 1–1.5 mm above the bud. It's important not to damage the bud's sheath; cutting too close will cause its death. Leaving a stump above the bud is also highly undesirable: it will dry out, and the weakened bud will become non-viable.
Pruning above the outer bud. Carried out at a 45-degree angle.0The lower cut should be level with the underside of the bud, and the upper cut should be 1–1.5 mm above the bud. It's important not to damage the bud's sheath; cutting too close will cause its death. Leaving a stump above the bud is also highly undesirable: it will dry out, and the weakened bud will become non-viable.
- When cutting branches, you must first make an undercut from below to avoid damaging the bark, and then cut the branch completely from above.
When cutting down large branches, it is necessary to leave a stump to avoid damaging the inner layers of the mother branch or leader, and only then cut the stump to a ring.
Common mistakes
The consequences of improper crown formation and errors made during pruning can cause irreparable damage and cost the apple tree its life:
- Crown density. Without proper pruning, branches touch each other, become damaged, and become more susceptible to disease. Fungal diseases often develop in dense crowns.
- Using an unsharpened tool damages the bark and prevents cuts from healing for a long time.
- Failure to time pruning correctly. If the time before sap flow begins in the spring is missed, pruning should be postponed until autumn, but under no circumstances should it be done while the buds are swelling.
- A stump left after pruning always dies and turns into dust, which creates a favorable environment for fungal diseases and pests. Stumps should be removed by the ring.
- Severe pruning of young trees promotes the development of numerous suckers and weakens the tree.
- Wound treatment. Do not apply clay, chemicals, or nitrocellulose paints to the cuts. The best way to treat the cut is to coat it with garden pitch after it dries.
Forming an apple tree's crown is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process. However, with the right approach, a healthy tree will not only bear high-quality fruit but also provide aesthetic pleasure from the appearance of a well-maintained garden.

 mandatory removal of weak shoots, competitors and
mandatory removal of weak shoots, competitors and 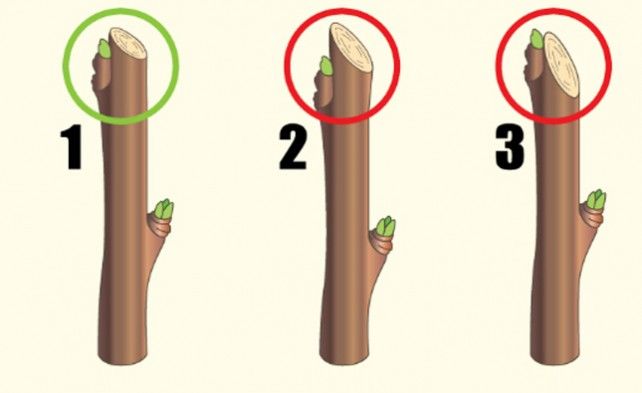 Pruning above the outer bud. Carried out at a 45-degree angle.0The lower cut should be level with the underside of the bud, and the upper cut should be 1–1.5 mm above the bud. It's important not to damage the bud's sheath; cutting too close will cause its death. Leaving a stump above the bud is also highly undesirable: it will dry out, and the weakened bud will become non-viable.
Pruning above the outer bud. Carried out at a 45-degree angle.0The lower cut should be level with the underside of the bud, and the upper cut should be 1–1.5 mm above the bud. It's important not to damage the bud's sheath; cutting too close will cause its death. Leaving a stump above the bud is also highly undesirable: it will dry out, and the weakened bud will become non-viable.







Comments
Interesting article, detailed.
I'm a beginner gardener and my plot is small. There's a vacant spot near the fence, and it's on the sunny side. I was racking my brain trying to figure out what to plant there. I thought only grapes were climbing plants, but they don't grow in our area. It turns out I could plant an apple tree there. That vertical palmette is a great idea. It suits me perfectly.
Many thanks to the author!
Tree pruning can create interesting shapes. I've long used various methods to give my garden a unique look. For example, near my hedge, I have a white plum tree growing not as a regular tree, but pruned into a vertical palmette, which covers most of the fence. Incidentally, apple trees grow well near a hedge, and harvesting the fruit is much easier this way. But it certainly takes some work to achieve this shape.
Who laid apple trees horizontally and which varieties are best to use for the molding?
Lots of useful information. But I'd like to read about pruning columnar apple trees, particularly varieties that require less maintenance. I'm shopping at the market, but I don't know which variety to choose. And sellers can be deceiving.