
Gum disease in fruit trees: treatment and prevention measures
The causes of gum flow have been studied for many years, but the main thing is still known: this process is an attempt by the affected tree to fight the disease on its own. It is also known that such self-treatment is ineffective. Therefore, the leakage of an amber-colored liquid from the trunk, branches, or fruit of a tree signals a problem and requires assistance.
Content
- The principle of gum flow
- Causes of gum flow and its prevention
- Mechanical damage to the bark
- Incorrect formative or sanitary pruning of a tree
- Mismatch of the variety with the climatic growing conditions
- Deficiency or excess of mineral and organic fertilizers
- Bacterial and fungal diseases
- Soil acidification
- Heavy clay soil
- Violation of the watering regime
- Damage to the bark by insect pests
- Frostbite of tree bark and sunburn
- Treatment
- Conclusion
The principle of gum flow
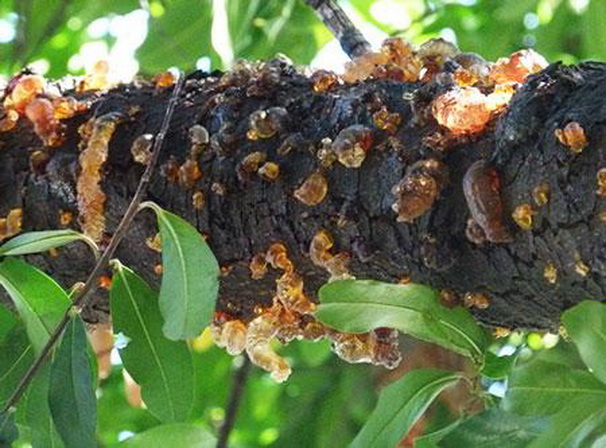

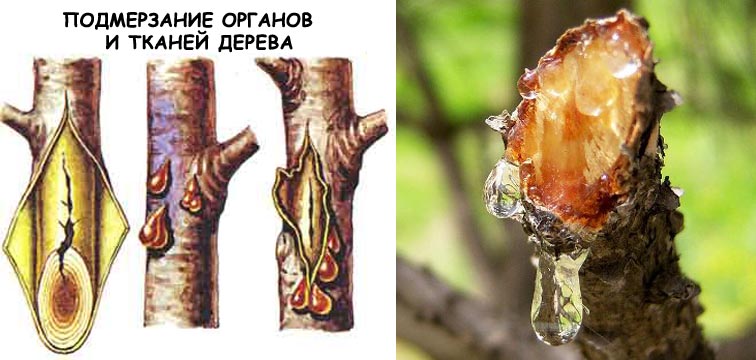
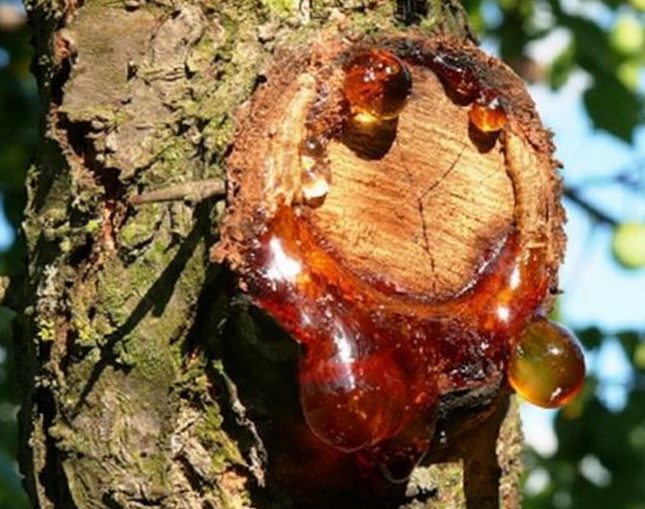
Gum flow (gummosis) is characterized by the secretion of a clear, amber-colored, thick, and sticky fluid from a hole in the bark called gum. The process is common in perennial plants, most often trees and shrubs.
Chemically, gum consists of calcium, magnesium, and potassium salts of various high-molecular organic acids. It is usually tasteless, but sweet or bitter exudates can also occur. Pure gum, unaffected by fungal diseases, is odorless.
Reasons for the formation of gum
Gum forms in the trunks, roots, branches, fruits, and seeds of plants, with starch, found in plant tissue, playing a significant role in this process. Excess starch causes the degeneration of tissues in the trunk core, cambium cells, the tree's vascular system, and the tree bark.
One of the reasons for increased starch in wood is the influence of external factors, another is the failure to observe agricultural practices and preventative measures to prevent fungal and viral diseases. In any case, gum formation pathological process of inflammation of wood tissues.
Most often, gummosis affects plums, cherries, sweet cherries, apple trees, peaches and apricots.
The process of gum formation is as follows:
- in the affected organic cell, the metabolism of minerals is disrupted and the amount of starch increases;
- the function of the cambium is disrupted, the cells do not form new wood, but turn into gum;
- as a result of the division of affected cells, new ones appear, containing excess starch;
- If the problem is not identified and corrected in a timely manner, healthy cambium cells are replaced by cells containing gum;
- Subsequently, the gum is released from the cell and fills individual sections of the vascular system of the trunk;
- areas of healthy cambium are destroyed, degenerating into gum, thereby increasing its quantity;
- The cambium tissue dies, the affected cells spread and pour out from a crack in the bark caused by mechanical damage or internal weakening.
Thus, the wound in the bark through which the gum flows is always quite deep.
Long-term gummosis not only significantly weakens the tree, but can also lead to the death of an individual section or the entire plant.
Causes of gum flow and its prevention
The main reasons for gum leakage are:
Mechanical damage to the bark

 Dangerous due to the possibility of penetration mushrooms and viruses into stem cells. If such a risk factor is detected, the following should be done:
Dangerous due to the possibility of penetration mushrooms and viruses into stem cells. If such a risk factor is detected, the following should be done:
- Use a sharp knife to clear the damaged area of dead bark tissue;
- if there is a damaged area of wood or a wound larger than 10 cm, cover the leaking area garden pitch, prepared on the basis of beeswax, which contains minerals that promote healing, and tightly wrap with strong cotton cloth;
- Cover minor damage with white oil paint on natural drying oil - this will prevent sap leakage and the development of rot.
Do not use preparations containing petroleum products or mineral oils to treat open wounds on tree bark, as they can cause tissue death and chemical burns.
Incorrect formative or sanitary pruning of a tree
 Using unsharpened tools, excessive pruning of branches, or failure to adhere to deadlines can lead to increased sap leakage, wound rotting, or decreased frost resistance of the tree.
Using unsharpened tools, excessive pruning of branches, or failure to adhere to deadlines can lead to increased sap leakage, wound rotting, or decreased frost resistance of the tree.
Adherence to the deadlines for removing excess shoots ensures timely healing of wounds:
 spring pruning is carried out in early spring before the sap begins to flow, but after the threat of recurrent frosts has passed;
spring pruning is carried out in early spring before the sap begins to flow, but after the threat of recurrent frosts has passed;- summer - as necessary, in case of appearance of unwanted shoots, however, it is not advisable to cut off skeletal branches;
- autumn – carried out no later than 1 month before the onset of frost.
The treatment of wounds resulting from pruning must be carried out using garden var.
Mismatch of the variety with the climatic growing conditions
 The selection of tree varieties for planting should be based on the region's climatic conditions. Mismatches in these conditions lead to the development of homosis for the following reasons:
The selection of tree varieties for planting should be based on the region's climatic conditions. Mismatches in these conditions lead to the development of homosis for the following reasons:
- high humidity at low temperatures;
- high air temperature in summer (more than +38 °C);
- low air temperature in winter (below -35 °C);
- dry hot wind;
- recurrent frosts in spring;
- prolonged thaws.
Varieties that are not adapted to such conditions will die sooner or later.
Deficiency or excess of mineral and organic fertilizers
 When applying fertilizer to the tree trunk circle, you should follow the general rules:
When applying fertilizer to the tree trunk circle, you should follow the general rules:
- Nitrogen-containing fertilizers should be applied only until mid-June or before flowering. Excess nitrogen stimulates the rapid growth of young shoots and green mass at the expense of wood maturation. This makes the tree vulnerable to various diseases, and its frost resistance is significantly reduced. Furthermore, nitrogen inhibits phosphorus absorption and displaces calcium.
- Fertilizers containing potassium and magnesium are recommended for application in the fall, after harvest, and in the spring, at the beginning of the season. Excessive amounts of these substances prevent calcium from being absorbed, which in turn leads to changes in the cambium structure.
Bacterial and fungal diseases

 The following diseases have a detrimental effect on young shoots, trunks, vascular system and cambium:
The following diseases have a detrimental effect on young shoots, trunks, vascular system and cambium:
- moniliosis;
- bacteriosis;
- black crayfish;
- Clusterosporiosis;
- perenosporosis.
An effective way to prevent fungal diseases is to spray the garden three times in the fall, after harvesting, and in the spring, from the beginning of sap flow until buds appear, with the following preparations:
- Bordeaux mixture;
- 1% solution copper sulfate;
- 3% solution of ferrous sulfate.
During the season, the tree can be treated with Mikosan B or Fitosporin.
Soil acidification
 Occurs naturally or as a result of excess potassium and magnesium. Soil neutralization should be carried out using the following substances:
Occurs naturally or as a result of excess potassium and magnesium. Soil neutralization should be carried out using the following substances:

- slaked lime;
- dolomite flour;
- chalk;
- shell rock;
- ground limestone;
- wood ash.
In addition to restoring soil pH, this procedure will increase the amount of available calcium.
Heavy clay soil
 Stagnant water in the soil leads to an excess of minerals in the wood, which leads to disruptions in cell formation. Furthermore, overwatering and heavy soil can lead to root rot and ultimately to the death of the tree.
Stagnant water in the soil leads to an excess of minerals in the wood, which leads to disruptions in cell formation. Furthermore, overwatering and heavy soil can lead to root rot and ultimately to the death of the tree.
The composition of clay soil can be improved by digging it and adding the following components:
- rotted manure – 1 part;
- fertile soil – 2 parts;
- rotted compost – 1–2 parts;
- river sand – 1 part;
- charcoal – 1 part.
It is important to constantly loosen the soil and promptly remove weeds from the tree trunk circle.
Violation of the watering regime
 A lack of moisture, just like an excess, prevents the normal absorption of potassium, phosphorus and calcium, which leads to a nutritional imbalance and, consequently, to disturbances in the normal development of wood.
A lack of moisture, just like an excess, prevents the normal absorption of potassium, phosphorus and calcium, which leads to a nutritional imbalance and, consequently, to disturbances in the normal development of wood.
Damage to the bark by insect pests
 The following insects cause damage to tree bark: bark beetle, scale insect, thrips, sap beetle.
The following insects cause damage to tree bark: bark beetle, scale insect, thrips, sap beetle.
Preventive measures include three treatments of trees and the trunk circle in early spring before the sap begins to flow and as soon as pests are detected with one of the following preparations:
- Iskra-M;
- Confidor Extra;
- "Vitalizer NV-101";
- "BI-58";
- "Corado".
Frostbite of tree bark and sunburn
 Whitewashing the trunk and skeletal branches will help protect the tree from sunburn. It's important to remember that this procedure should be carried out in the fall after the leaves have fallen, but at above-zero temperatures. Whitewashing can also be done in the spring, after the threat of frost has passed.
Whitewashing the trunk and skeletal branches will help protect the tree from sunburn. It's important to remember that this procedure should be carried out in the fall after the leaves have fallen, but at above-zero temperatures. Whitewashing can also be done in the spring, after the threat of frost has passed.
To prevent freezing, simply wrap the tree trunk in cardboard, burlap, or spruce branches and secure it tightly. In early spring, remove the covering to prevent bark rot. This protection will also protect the tree from rodents.
Treatment
When the first signs of gummosis are detected, it is necessary to begin searching for the cause and eliminating the gummosis. It is important to remember that the treatment of a branch and a trunk has some differences.
Treatment of the trunk
 The bark removal procedure should be carried out at an air temperature of at least +10…+12 °C in the following order:
The bark removal procedure should be carried out at an air temperature of at least +10…+12 °C in the following order:
 clean the leak site with a sharp knife;
clean the leak site with a sharp knife;- remove all damaged bark;
- cut out the affected wood to the base, leaving no darkened areas;
- carefully treat the wound with the drug "Filolavin", "Sporobacterin", "Fitosporin M", "Agat" or "Gamair", leave to dry for 2-3 hours;
- in the next 4 hours, treat the injury with juice of common sorrel or horse sorrel 3-4 times;
- cover the damaged area with garden pitch and wrap it with thick cotton cloth;
- water tree with a solution of calcium chloride, diluted according to the instructions;
- After 5–7 days, start watering with a weak pink solution of potassium permanganate and continue this throughout the season;
- begin to eliminate the problem that caused gummosis.
Wood removal should only be carried out after the sap flow period has ended!
Branch treatment
 Branch treatment does not cause serious damage to the tree and is carried out in the following order:
Branch treatment does not cause serious damage to the tree and is carried out in the following order:
- cut off the damaged branch to the ring;
- clean the wound with a sharp knife, removing all damaged wood;
- disinfect the wound twice with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and leave until completely dry;
- Cover the damaged area with garden pitch and wrap it in thick cotton cloth.
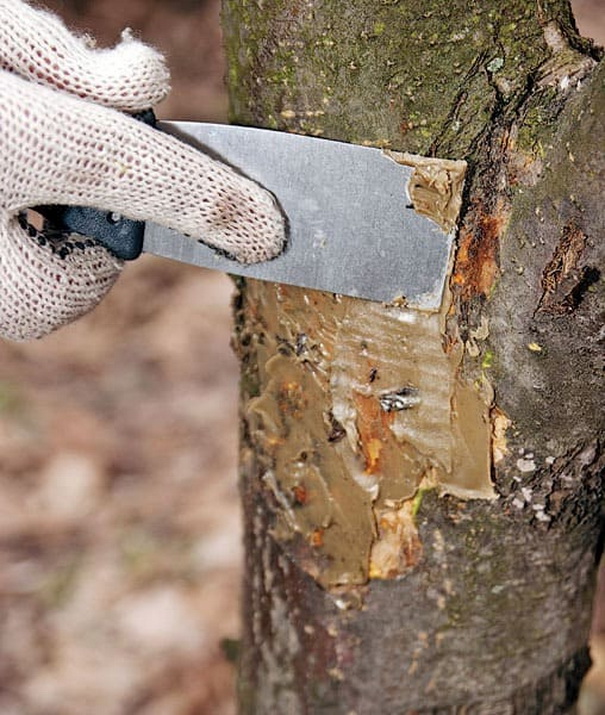

When removing branches, it is important to examine the area cut – it must be clean. If affected wood is present, the next lower-order branch is removed. If a first-order scaffold branch is affected, it is removed and the trunk is treated.
Leaving hardened gum on the bark as a natural protection is only possible if there is absolute certainty that gummosis began due to mechanical damage.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a serious problem, but it's also easily avoidable. It's important to follow proper agricultural practices, eliminate pests promptly, and take care of your garden during the cold season.
 spring pruning is carried out in early spring before the sap begins to flow, but after the threat of recurrent frosts has passed;
spring pruning is carried out in early spring before the sap begins to flow, but after the threat of recurrent frosts has passed;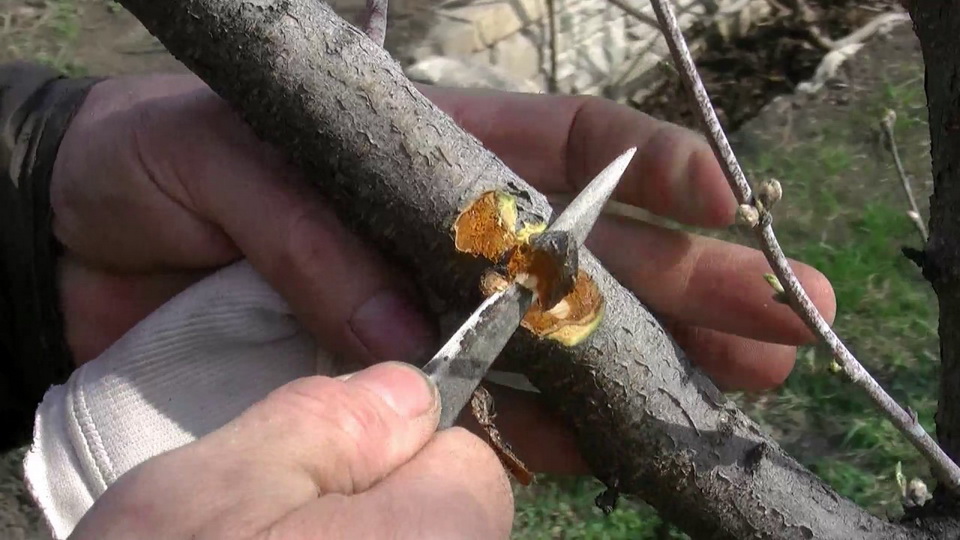 clean the leak site with a sharp knife;
clean the leak site with a sharp knife;






