
How to save an apple tree if hares have chewed the bark in winter
When exploring an orchard after winter, you'll often notice damaged tree bark. Hares and mice, searching for food, are tempted by the tender bark of young saplings, especially apple trees. By peeling off strips of bark, these forest visitors reach the succulent bast, causing significant damage to the trees. Damage to the vascular cells stops sap flow, leading to the death of the plant. This article will explain how to save a tree from death and protect your orchard from harmful rodents.
Content
Tree treatment
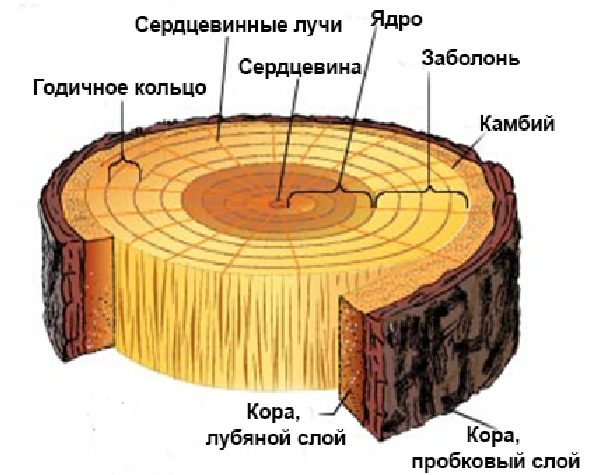 Hare damage typically occurs at snow level. Young saplings can lose their tops completely, while older trees typically suffer damage to lower branches or the trunk bark. Treatment depends on the severity of the damage. Superficial bark damage is considered the mildest. In this case, the cambium—the layer between the bark and the main wood—remains intact, so healing is relatively straightforward. However, if the bark is gnawed away completely around the trunk and to a significant depth, there is a high risk of tree death. In such cases, rapid, drastic measures are necessary.
Hare damage typically occurs at snow level. Young saplings can lose their tops completely, while older trees typically suffer damage to lower branches or the trunk bark. Treatment depends on the severity of the damage. Superficial bark damage is considered the mildest. In this case, the cambium—the layer between the bark and the main wood—remains intact, so healing is relatively straightforward. However, if the bark is gnawed away completely around the trunk and to a significant depth, there is a high risk of tree death. In such cases, rapid, drastic measures are necessary.
Note: The cambium is responsible for bark growth and proper sap flow. Damage to the thin cambium layer leads to the death of the tree.
Treatment of superficial single lesions
Minor damage to the bark is recommended to be treated immediately after detection with a mixture of clay and cow manure or garden pitchYou can also use a ready-made antibacterial product. After treatment, wrap the trunk in plastic or cling film to speed up the healing process and protect the tree from infection. It is recommended to apply roofing felt over the film to protect the healing bark from direct sunlight. As summer approaches, the wound heals, and the dead tissue falls off.
 If the inner layer, the cambium, has dried out as a result of damage, healing will require more effort and time. The wound requires constant care until the edges of the damaged area are completely closed and a dense scar forms on the bark. The surface of the growing layer is periodically scratched to stimulate new tissue growth and coated with garden pitch. This process can continue for 2-3 years.
If the inner layer, the cambium, has dried out as a result of damage, healing will require more effort and time. The wound requires constant care until the edges of the damaged area are completely closed and a dense scar forms on the bark. The surface of the growing layer is periodically scratched to stimulate new tissue growth and coated with garden pitch. This process can continue for 2-3 years.
In severe cases of apple tree bark damage caused by hares, products known as "artificial bark" are used. Artificial bark is a special mixture that accelerates regeneration processes during wound healing. The biologically active substances contained in the product stimulate the tree's own regenerative powers. The resulting elastic film adheres firmly to the wood and holds tightly, just like real bark. Furthermore, this sealant protects the treated areas from water penetration and drying out.
If tree wounds were noticed in winter, it is recommended to insulate the trunk with polyethylene or agrofibre. Treatment should only begin once the weather warms up.
Garters
Small fresh wounds with intact cambium can be healed using dressings with various medicinal agents:
- ointments "Heteroauxin";
- linden decoction (200 g of dried flowers per glass of water, boil, cool and strain);
- clay mash prepared from clay and manure in a ratio of 6:4;
- ready-made product "Rannet";
- 3% solution copper sulfate.
An ointment (linden blossom infusion, copper sulfate solution) is applied to the injured area, then covered with garden pitch, followed by a bandage made of cloth and plastic. A clay slurry is applied to the wound in a thick layer, dried, wrapped in cloth, and covered with clay again. Unlike the previous substances, ready-made bactericidal preparations, in addition to healing the wound, form a protective film on its surface. Therefore, wrapping the trunk with plastic or cloth is not necessary. The tree is left in this state until winter, and sometimes until the following spring, until a new cambium layer and bark form.
Radical treatment measures
Radical measures for treating trees include:
- grafting of new bark;
- wound grafting with a "bridge";
- cut trunk to grow back.
Let us consider in more detail the features of each of the listed methods.
Engraftment of the bark
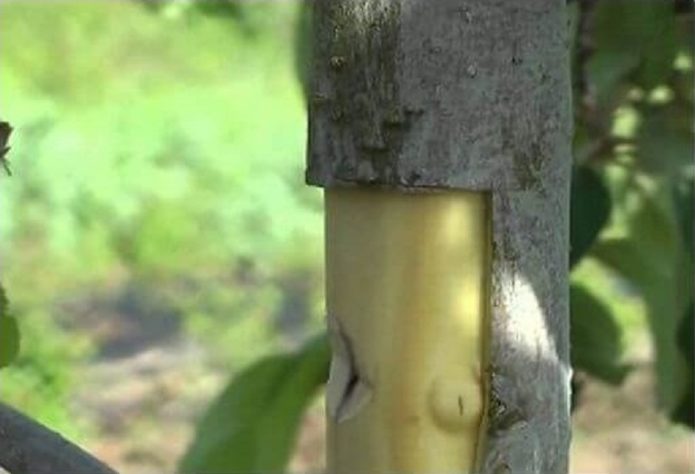 The method of grafting new bark taken from other parts of the tree is not particularly popular. It can be used only if the cambium layer is alive. If this layer is absent, grafting will be impossible. Furthermore, this technique does not guarantee success, even with extensive gardening experience. The main difficulty lies in ensuring the best possible adhesion of the bark.
The method of grafting new bark taken from other parts of the tree is not particularly popular. It can be used only if the cambium layer is alive. If this layer is absent, grafting will be impossible. Furthermore, this technique does not guarantee success, even with extensive gardening experience. The main difficulty lies in ensuring the best possible adhesion of the bark.
Step-by-step instructions for grafting bark onto an apple tree trunk:
- Using a sharp knife, cut the bark to be replanted from a thick tree branch or another plant of the same variety. The cut piece should be 10 cm larger than the affected area.
- The new bark is applied to the damaged area so that it completely covers it with a small margin on each side.
- The “patch” is tightly secured with tape or electrical tape.
- Carefully look after the sick tree: water it, feed it, prune it, and completely remove the ovary.
- For the winter, the tape is removed and the apple tree is protected in the usual way.
Bridge grafting
 A more reliable method is considered to be grafting the wound with cuttings. This method is more labor-intensive, but the results are almost always excellent. It is used when the bark is damaged all over the trunk or the wound occupies more than half the diameter. In this case, the damaged bark is temporarily replaced by cuttings, which are young shoots of the same plant. They are cut in early spring, while the tree is dormant and sap has not yet begun to flow. The length of the cuttings should be 15 cm longer than the width of the wound, ensuring that it completely covers it with a little extra.
A more reliable method is considered to be grafting the wound with cuttings. This method is more labor-intensive, but the results are almost always excellent. It is used when the bark is damaged all over the trunk or the wound occupies more than half the diameter. In this case, the damaged bark is temporarily replaced by cuttings, which are young shoots of the same plant. They are cut in early spring, while the tree is dormant and sap has not yet begun to flow. The length of the cuttings should be 15 cm longer than the width of the wound, ensuring that it completely covers it with a little extra.
Step-by-step instructions for bridge grafting:
- The damaged area is cleaned down to bare wood, cutting off any uneven areas from the bark.
- The trunk is treated with a 3% solution of copper sulfate.
- Cuttings of equal length are cut.
- The ends of the twigs are cut at a sharp angle and all the buds are removed from them.
- T-shaped cuts are made in the bark above and below the damaged area.
- The cuttings are inserted into the cuts, trying to secure them at the maximum depth.
- The cuts with built-in “bridges” are coated with garden pitch and tightly wrapped in polyethylene.
The older the apple tree, the larger its trunk diameter. This means that more cuttings will be needed to save it than for a young tree.
Trunk cut for reverse growth
 The most radical method of all the above. It's used in cases of extensive bark damage caused by hares, when there's no other chance of saving the tree. It involves completely cutting the plant down to its lowest point before the sap begins to flow. To prevent the tree from growing again this year, the location cut Cover with garden pitch. Provided the root system is well-developed and healthy, the apple tree will produce new shoots and resume growth next year. The strongest shoot is selected from the resulting shoots, which will become the new apple tree. The remaining shoots are destroyed.
The most radical method of all the above. It's used in cases of extensive bark damage caused by hares, when there's no other chance of saving the tree. It involves completely cutting the plant down to its lowest point before the sap begins to flow. To prevent the tree from growing again this year, the location cut Cover with garden pitch. Provided the root system is well-developed and healthy, the apple tree will produce new shoots and resume growth next year. The strongest shoot is selected from the resulting shoots, which will become the new apple tree. The remaining shoots are destroyed.
This method is used on trees older than 5 years, since young seedlings have a poorly developed root system and will not be able to withstand such a radical treatment method.
Prevention and protection of trees
Treating trees damaged by rodents is a rather laborious process that doesn't always guarantee a positive outcome. Moreover, once damaged, a tree permanently loses some of its fertility, so a high yield can't be expected. Therefore, it's recommended to keep rodent prevention in mind year-round. To protect your orchard during the winter, experts recommend a number of preventative measures.
- Whitewashing tree trunks with lime not only in spring, but also before winter to a height of about 1 meter.
- Autumn processing of tree bark and tree trunks cleared of fallen leaves, Bordeaux mixture or a solution of copper sulfate (at the rate of 100 g of substance per 10 liters of water).
- Wrapping with polyethylene or roofing felt for the winter.
- Protect young trees by placing cut plastic bottles on the trunk.
- Treating the trunks and lower branches with a mixture of naphthalene and fish oil (1:8), which also helps repel unwanted guests.
- Mulching the tree trunk circle with sawdust moistened with a solution of sanlisol, which will certainly drive away mice and hares.
- Using fine-mesh chain-link fencing and spruce and pine branches for mechanical protection. The trunks of young apple trees are wrapped in these materials to prevent animals from physically approaching them.
- Insulation of apple trees with non-woven materials.
- Trampling down snow around trees in winter prevents rodents from making passages and getting close to the trunk.
- Timely implementation of agricultural measures: digging, weed control, removal of fallen leaves and debris.
Video
Watch this video for practical advice on treating fruit trees damaged by rodents.
Conclusions
Young orchards often suffer damage from rodents. These wounds disrupt the integrity of the inner conducting layer of the bark, the cambium, which is essential for sap flow and the tree's life. If left untreated, these wounds can lead to the death of the plant. Therefore, it is recommended to immediately begin treatment using the methods described in this article, as well as implement preventative measures to protect the orchard.








