Zhelannoye apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Reds |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Summer |
| Size of apples | Average |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Tall tree |
| Shelf life | Low shelf life |
| Application | Fresh , For recycling |
| Winter hardiness | Average winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | From 5 years old |


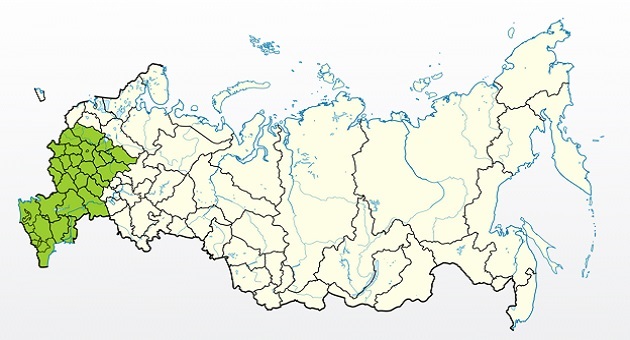 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
- Middle zone.
- Moscow region.
- North Caucasus.
- Leningrad region.
- Crimea.
- Some northern regions.
Origin
The apple tree's development began in the early 1990s at the All-Russian Research Institute of Fruit Crop Breeding. It was based on the North American McIntosh variety, which was open-pollinated. Finally, in 1999, an application for admission to official variety testing was first submitted. The authors are considered to be Zoya Mikhailovna Serova, Evgeny Nikolaevich Sedov, and Nina Glebovna Krasova.
In 2002, the variety was included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements and zoned for the Central Black Earth Region. In fact, Zhelannoye is successfully cultivated throughout the central zone, as well as in the southern and northern regions.
Content
Description of the Zhelannoe variety
 This apple tree was immediately appreciated by gardeners for the high consumer and commercial quality of its fruit. They are quite large, attractive, red-sided, fragrant, and very tasty. They are easy to transport over long distances and can be stored for quite a long time, considering that this is a summer variety.
This apple tree was immediately appreciated by gardeners for the high consumer and commercial quality of its fruit. They are quite large, attractive, red-sided, fragrant, and very tasty. They are easy to transport over long distances and can be stored for quite a long time, considering that this is a summer variety.
The trees are tall, making maintenance and harvesting difficult. They require regular pruning and plenty of space. These apple trees are easy to grow, have moderate frost resistance, and are rarely affected by infections. They are recommended for individual cultivation in home gardens and in intensive commercial orchards.
Apples: What do they look like?
 The fruits are generally medium or slightly smaller than average in size, weighing 90-160 grams. They are round, smooth, with wide, rounded ribs, and can be flattened along the central axis. They are symmetrical or slightly slanted, and uniform in size. There is no lateral seam.
The fruits are generally medium or slightly smaller than average in size, weighing 90-160 grams. They are round, smooth, with wide, rounded ribs, and can be flattened along the central axis. They are symmetrical or slightly slanted, and uniform in size. There is no lateral seam.
The skin is thick and, as it ripens, becomes covered with a dense waxy coating, giving the apple a silvery-gray hue. It is smooth, shiny, and glossy, with a greenish-yellow base color that becomes light yellow and whitish as it ripens. The blush is a fuzzy, translucent, crimson-red, covering 85% or more of the surface and featuring a distinct, ruby-colored, striped and speckled pattern. Subcutaneous punctures are numerous; they are gray and clearly visible on the surface. The easiest way to assess the chemical composition is to understand the basic indicators:
- P-active substances (catechins) – 380 milligrams.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 13.8 milligrams.
- Fructose (total sugars) – 10.8%.
- Pectins – 13.6%.
- Titratable acids – 0.61%.
The fruit's flesh is medium-dense, very juicy, fine-grained, very tender, and crispy, easily breaking off. It is white or has a slight creamy-yellow tint. The aroma is light and pleasant, and the flavor is spicy, sweet and sour, considered a dessert-like, balanced, and harmonious. Professional tasters have rated the fruit 4.6 and 4.8 out of 5 for appearance and flavor.
Zhelannoye apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 The trees are tall, with an oval or rounded crown, which does not become spreading over the years, but remains neat. They can easily reach 6-8 meters, and even more under favorable conditions without pruning. The branches are thin, crooked, set at right angles to the trunk, covered with greenish-brown, slightly pubescent bark; on the trunk, the bark is gray and prone to cracking.
The trees are tall, with an oval or rounded crown, which does not become spreading over the years, but remains neat. They can easily reach 6-8 meters, and even more under favorable conditions without pruning. The branches are thin, crooked, set at right angles to the trunk, covered with greenish-brown, slightly pubescent bark; on the trunk, the bark is gray and prone to cracking.
The leaves are medium to large, short-pointed, smooth, leathery, dense, and matte, with a tomentose pubescence on the underside. The nerves are rough, the edges are serrate-crenate, and serrated; their color can range from green to dark emerald. The root system is predominantly fibrous, deep, and branched, well adapted to seeking water in the soil.
Productivity and pollination
The variety is considered high-yielding, early-bearing and fast-growing.
A single tree typically yields quite a lot of fruit per season, over 100-140 kilograms. With proper, timely care, regular fertilizing, and, most importantly, favorable conditions, fruit yield can be increased by 25-50%.
Zhelannoye is considered a conditionally self-fertile variety. If there are no apple trees within 50-110 meters, the yield will be 15-25% of the maximum possible. To increase this yield, external pollinators should be chosen at the right time for the flowering period. It's a good idea to spray the trees with sugar or honey syrup during flowering, and also to bring beehives to the plantings during this time.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
Apple trees have moderate to high frost resistance, but at temperatures below -36-37°C, they suffer approximately 1.1 frost damage points. This allows them to be grown throughout virtually the entire temperate zone and even in more northern regions, not to mention warm and temperate climates.
Zhelanny has no genetic immunity to any disease. However, its resistance to all diseases, whether fungal, parasitic, or bacterial, is quite high. If the necessary preventative measures are taken promptly, infections can be completely eliminated.
Rootstocks and subspecies
The Zhelannoye variety doesn't yet have any subspecies, but many gardeners have adopted the habit of cultivating it on dwarf and semi-dwarf rootstocks. This allows trees to grow no more than 2.5-3.5 meters tall, significantly facilitating care and harvesting. It also saves space in the garden, as the trees only need a spread of 2.5-3 meters in diameter.
Features of growing Zhelanny
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- Apple trees don't like high groundwater levels because their roots penetrate deep. They can reach the moisture, which will inevitably cause rot.
- Open, sunny spaces are always best for fruit trees, and the Zhelannoye apple variety is no exception. It can even grow in the shade, but the tree will be weak, spindly, and may not bloom or bear fruit for many years.
- The soil can be of any quality (sandy loam, podzolic soil, black soil, clay), but it must be neutral, that is, not excessively acidic or saline.
- No tree likes drafts, so you need to make sure that good ventilation does not damage the apple trees.
- Planting holes should be prepared at least 4-6 weeks before planting. Dig holes 60-70 centimeters deep and 1-1.2 meters in diameter, add fertilizer to the bottom (usually organic, but mineral fertilizers are also acceptable), cover with a drainage layer or soil, and water with 35-50 liters of water. Leave the holes outdoors.
- For tall apple trees, leave at least 5-6 meters of distance between the holes, and for dwarf apple trees, 2.5-3 meters is enough.
- It's a good idea to immediately drive or dig stakes into the planting holes to tie the young trees to. These stakes can be made of metal, wood, or plastic. They shouldn't be removed until 2-3 years after fruiting begins.
- The seedlings are placed in warm water or a mixture of soil and water for 5-6 hours, after first inspecting the rhizome and cutting off all unnecessary (dry, broken) shoots.
- The root collar should always be left above the surface. This is important to consider immediately when planting, as the soil will usually settle and the trees will need to be replenished.
- Place the tree on drainage, straighten the roots, sprinkle with soil and compact it by hand, water with 20-35 liters of water.
Landing dates
The optimal time to plant apple trees is in the spring, around mid-March or early April. It's important to ensure that the soil has warmed by this time and that the threat of frost has passed. In warmer regions, planting in the fall is acceptable, but at least 4-5 weeks should pass before the first frost. Concealed rootstocks can be planted at any time during the growing season.
 Tree care
Tree care
Protection from frost and pests
Trees need to be prepared for winter. Watering should be stopped in August. Just before frost, the trunk and skeletal branches should be cleaned of loose bark with a stiff brush, pruned, wounds sealed with pitch, and the trunks whitewashed with lime.
You can surround the trees with straw, wrap them in old tights or burlap, or scatter spruce branches over the root zone. In some cases (dwarf trees), trees can be covered using a tent-like method, but this is not possible for tall, mature trees.
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Dig around the tree trunk in spring and fall, but carefully, not going deeper than 8-10 centimeters, otherwise you could damage the roots. At the same time, remove all weeds, root suckers, and shoots from other plants. At other times, you can hoe the soil, for example, the day after glazeso that it doesn't form a tight lump.
Watering In the first year, you'll need about 10-20 liters per trunk per week. You can split this amount and apply water in the morning and evening. If possible, arrange for sprinkler or drip irrigation. watering, such options are most suitable for apple trees.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
The variety's branches grow sparsely, so the trees are usually trained in the nursery, leaving only the crowns to be maintained. The best form is a sparsely tiered one, with shoots spaced widely apart at different heights.
Sanitary pruning helps remove broken, diseased, or dead branches that don't provide any benefit but instead drain the tree's sap. It's best to prune them in the spring, and if necessary, in the fall. However, shoots broken by wind or under the weight of fruit should be removed immediately, and the wound should be sealed. garden pitch.
Pollinator varieties
- Slav.
- Antonovka.
- Saffron pepin.
- Autumn cinnamon (Susleipskoe).
- Korobovka.
- Stark Erlist.
- Borovinka.
- Bellefleur the Chinese.
Reproduction
- Layers.
- Grafting cuttings.
- Clones.
- Growing from seeds.
Ripening and fruiting Desired
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
This variety can't be called particularly early-fruiting, although it is considered so. Tall varieties produce their first harvest only 6-8 months after planting in open ground. The fruit yield is quite small, approximately 3-4 kilograms, and full fruiting will take some time. Dwarf and semi-dwarf varieties begin producing apples much earlier, as early as 2-3 years. They yield much fewer apples, but it's worth trying.
Flowering time
Summer apple trees typically bloom early, and the Zhelannoye apple tree also opens its buds in early May or during the first ten days, even before the fifteenth. The process continues for about one to two weeks, and by the end of May, it has completely subsided, with ovaries forming. The flowers are large, beautiful, closed, and cup-shaped, but open almost completely flat. They are fragrant, white-pink with a lilac-purple tint when closed, and a soft pink when open.
Fruiting and growth
Trees grow at a moderate rate. They can reach approximately 50-60 centimeters a year before fruiting, but the rate slows slightly after the apples begin to ripen. Nevertheless, they quickly reach their maximum height and begin producing full crops as early as 9-12 years. Their active lifespan is over half a century.
Apples begin to ripen already at the end of the first ten days August In warmer regions, and a little later in colder regions. All fruit must be picked by the end of the month, otherwise it may fall to the ground. They don't keep for long, only 4-6 weeks in a suitable cellar or special refrigerator. After that, they wilt, lose flavor, become soft and fluffy, lack juiciness, and rot. Therefore, it's best to process or eat them immediately to avoid wasting the harvest.
Top dressing
- Compost.
- Manure.
- Superphosphate.
- Chicken manure.
- Wood ash.
- Ammonium nitrate.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Inspect for diseases or pests.
- Limit or increase watering.
- Feed or apply fertilizer.
- Transplant to a sunny place.
Why do apples fall?
- Natural weather conditions (wind, rain, hurricane, hail).
- Pest damage.
- Diseases.

Share your own experience with the Zhelannoe apple variety so that any gardener can learn about it before planting and achieve maximum results.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting