
How to plant apple and pear trees in spring: rules, distances, methods
Proper planting of fruit trees determines their future growth and development, including their immunity, the onset of fruiting, and yield. The optimal time for planting apple and pear trees is after the leaves have fallen or after the snow has completely melted.
Content
Suitable times for planting apple and pear trees
The timing of planting pear and apple trees depends on the variety and the climate of the region. In southern regions, planting trees during a warm and fairly long autumn yields good results. Relatively mild winters do not impede normal root development. By early spring, the seedlings have already formed new roots capable of intensively absorbing and assimilating beneficial micronutrients and vitamins from the soil.
In the middle latitudes, these crops are planted in September or in the period from the end of April to the end of the first ten days of May, at this time soil It's already completely thawed. Experts recommend doing this before the buds swell and before the leaves begin to unfurl, when the trees have not yet entered their active growing season. Otherwise, the natural growth cycle will be disrupted.
When planting seedlings at other times for any reason, it is necessary that their roots be with a lump of earth.

In northern regions, characterized by short autumns and long, harsh winters, planting times are shorter. Autumn work with bare roots should be completed a month before the ground freezes.
Recommended planting times
Apple and pear trees are typically planted in the fall and spring. Pears, which require more care and growing conditions, are planted first, followed by the relatively easy-to-grow apple trees. A significant advantage of fall planting (from the second half of September to the end of October) is that during this period, the plants are no longer able to vegetate, and their entire activity is focused solely on root growth.
Features of spring planting
Spring is the most favorable time for planting apple and pear trees. This is determined by the following reasons:
- no risk of freezing of the root system, which eliminates the need to restore the vital resources of fruit crops;
- minimal exposure of trees to stress, since temperatures above +10 °C are favorable for the rapid adaptation of seedlings to new conditions;
- abundantly moist soil promotes good survival.
Seedlings with closed root system It is permissible to plant from April to October.
Spring planting dates in different regions
Apple and pear planting dates vary depending on the region's climate: in the south, such work begins earlier than in northern regions. Typically, the following schedule applies:
- in the southern regions – from the second half of March to the end of April;
- in the middle zone - from the end of April to mid-May;
- in areas with severe winters (Siberia And Ural) – from the beginning of May until the first days of June.
According to the lunar calendar
The optimal day for planting seedlings can be chosen using the lunar calendar. In 2020, the following are favorable days for spring work according to the lunar calendar:
- March – from 26 to 29;
- April – from 11 to 15, 24, 25;
- May – from 2 to 10.
Often, for one reason or another, it's not possible to plant seedlings on the specified dates. In this case, planting can be done at any time, with the exception of unfavorable dates indicated in the lunar calendar. These include the days of the new moon and full moon, as well as the period when the moon is in Aquarius, which is considered barren.

In 2020, unfavorable days for planting pears and apple trees are as follows:
- March – 9, from 19 to 21, 24;
- April – 8, from 15 to 17, 23;
- May – 7, 13, 14, 22;
- June – 5, 9-11, 21.
Algorithm for spring planting of apple and pear trees
Careful preparation for planting fruit crops is the key to their rapid adaptation and rooting.
Principles of seedling selection
When choosing planting material, it's important to choose varieties that have proven themselves in a specific region. This means they should have sufficient winter hardiness for the local climate.
Beginners are advised to purchase seedlings in a container (with a closed root system).
High-quality planting material must meet a number of criteria:
- absence of signs of wilting, damage by diseases and harmful insects;
- age not older than 2 years, capable of quick adaptation;
- height – from 1 to 1.5 m (a deviation upwards or downwards indicates improper care when growing seedlings and an excess of nitrogen fertilizers in the soil);
- the presence of a complete and well-developed root system (without any new formations); in addition to the main root, the presence of several roots located on the sides is necessary.
The fact that the tree is truly a varietal one is indicated by the grafting site located at the bottom of the trunk.
The wood on the upper part of the trunk should be mature and free from mechanical damage, as well as cracks caused by sun exposure. burns or temperature fluctuations. Furthermore, any barrel distortion is unacceptable.
When purchasing seedlings with an open root system, it is advisable to choose specimens that are in the dormant phase and do not show signs of the beginning of vegetation, for example, open buds or formed leaves.
Preparing for landing
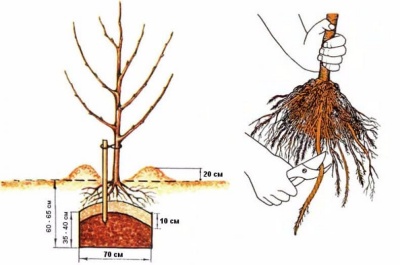 Immediately before placing the seedling in the prepared hole, the old soil is washed off its roots, and then they are dipped in a clay slurry. Next, the roots are trimmed slightly to refresh them, and any overly long or damaged roots are removed.
Immediately before placing the seedling in the prepared hole, the old soil is washed off its roots, and then they are dipped in a clay slurry. Next, the roots are trimmed slightly to refresh them, and any overly long or damaged roots are removed.
Experienced gardeners recommend soaking seedlings in water with Kornevin added for several hours (preferably a day). This will promote rapid restoration of biological processes in the root system and nourish it with moisture.
Choosing a suitable location in the garden
Planting apple and pear trees in the optimal location is an important factor for their continued successful development. These trees thrive best in sunny areas free from drafts. Preferably, a north-facing site sheltered from winds that can be extremely drying in winter. The tree should be planted on the south side, ensuring maximum sunlight.
In lowlands, it is advisable to plant fruit crops in elevated areas, preventing moisture from accumulating near the root system.
When choosing a site, consider the groundwater table: it should be 1.5 meters or more below the ground surface. If the water table is close, seedlings are planted on pre-made mounds.
You should not plant pears and apple trees near trees with spreading crowns, as this will negatively affect their full growth and fruiting.
Recommended landing distance
 The spacing between rows and the fruit trees themselves has a significant impact on the lifespan of the trees and their yield. Therefore, young apple and pear trees are planted according to a specific pattern, taking into account their crown growth and vigor:
The spacing between rows and the fruit trees themselves has a significant impact on the lifespan of the trees and their yield. Therefore, young apple and pear trees are planted according to a specific pattern, taking into account their crown growth and vigor:
- on a vigorous rootstock – 5–7 m;
- on medium-sized trees – 3–4 m;
- on low-growing – 1–3 m.
Columnar varieties are best planted according to the following pattern: 1 m between rows and ½ m within a row.
For closely planted crops, it is necessary to regularly adjust the crown, including not neglecting summer pruning.
Soil characteristics
Apple and pear trees grow particularly well in loamy soils, but if certain rules are followed, growing crops in black soil and sandy loam soil is permissible:
- For planting on sandy soil, the holes are made wider and the soil is mixed with compost or peat.
- On clay soil, trees are planted at a depth of no more than 50 cm, and the planting hole is formed in the form of a small trench so that the bottom is inclined towards the ditch.
- When planting on clay and sandy soils, it is essential to provide a high-quality drainage system to allow the trees to thrive in such conditions.
The ideal soil for growing pears and apple trees should be light, loose, with a neutral acidity level, capable of warming up quickly, and have excellent moisture and air permeability.
When planting fruit crops in sandy soil, it is recommended to add a large amount of compost and a little clay, and sand will help balance the composition of clay soil.
Preparing a hole for planting
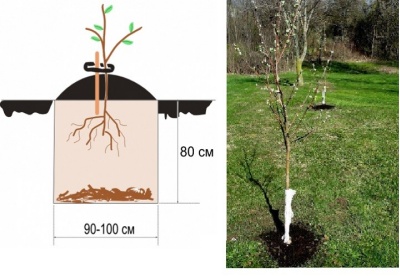 For spring planting, it's best to prepare planting holes in the fall to allow the soil to settle to the desired level, at most 14 days before planting. Since the topsoil will be used later, it's discarded when excavating. Holes can range in depth from 50 to 80 cm, and their width from 60 to 100 cm. When planting seedlings with closed root systems, holes are typically made 2-3 times larger than the container.
For spring planting, it's best to prepare planting holes in the fall to allow the soil to settle to the desired level, at most 14 days before planting. Since the topsoil will be used later, it's discarded when excavating. Holes can range in depth from 50 to 80 cm, and their width from 60 to 100 cm. When planting seedlings with closed root systems, holes are typically made 2-3 times larger than the container.
The bottom of the pits is lined with a 15 cm drainage layer consisting of small stones or broken bricks, and a nutritious soil mixture is poured on top of it.
When growing apple and pear trees in clay soil, it is necessary to form planting holes with maximum depth and be sure to lay a drainage layer in them.
Preparation of nutrient substrate
 The soil mixture intended for filling planting holes should contain several components:
The soil mixture intended for filling planting holes should contain several components:
- 20–30 cm of the top fertile soil layer removed during digging;
- up to 16 kg of high-quality compost or humus;
- 9 kg of sand (if the soil is heavy);
- 9 kg of non-acidic peat;
- 600 g bone meal, ½ kg superphosphate;
- 200 g of potassium sulfate or 400 g of wood ash.
Instead of potassium sulfate and superphosphate, it is permissible to use nitroammophoska in the amount of 400 g or diammophoska.
When planting trees, avoid applying nitrogen fertilizers, as they promote vegetation while slowing down the development of the root system.
Planting technique
Planting of fruit crops is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- the prepared hole is filled with nutritious soil mixture, leaving a depression corresponding to the size of the seedling’s roots;
- a wooden stake is driven in near the hole, which will be used as a support for the young tree;
- Place the planting material in the center of the mound in the hole, straighten its roots and sprinkle them with soil, periodically shaking the seedling to prevent the formation of voids;
- compact the soil, water the tree trunk circle (2-3 buckets under each trunk) and lay out a layer of mulch (peat, compost, humus).
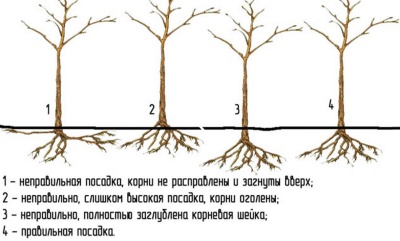
After landing, it is important to check the location root collar: it should be located above the soil surface by about 3-5 cm.
Planting trees near groundwater
If the groundwater level is no deeper than 1.5 meters, planting in pits is not recommended. In this case, mounds 1 meter or more high (depending on the water table) and 3 cm in diameter should be formed for planting.
Rules for caring for planted trees
 After planting, fruit crops require regular care, which includes a number of activities:
After planting, fruit crops require regular care, which includes a number of activities:
- pruning – the first procedure is carried out immediately, shortening the top of the seedling by 15–20 cm;
- weeding – removing weeds in and around the tree trunk circle;
- loosening the soil to prevent the formation of a crust that disrupts metabolic processes in the soil;
- watering with a frequency of once every 10 days, the event is carried out in the evening.
After spring planting, trees don't require fertilizing until midsummer. In July, a potassium solution prepared at a ratio of 1 teaspoon per 10 liters of water is added to the soil. No other fertilizers are used during the current season.
If the seedling blooms in the first year after planting, the formed inflorescences are carefully removed to allow the tree to quickly establish itself in its new location.
Seedlings planted in spring adapt much better than those planted in fall, as they are exposed to warm conditions for a longer period. To stimulate this process, it's important to follow all agricultural practices.








