
Planting an apple tree in the spring in the Leningrad region: step-by-step instructions
Apple trees are among the most common fruit trees in Russian gardens. They thrive in all regions, adapting perfectly to the climate of each part of the country. Regionalized varieties are particularly well-suited to the humid and cool weather of the Leningrad Region.
Content
Suitable varieties for the Leningrad region
Young seedlings must be selected taking into account all climate conditions, soil characteristics, and groundwater depth. Based on ripening times, summer, autumn, and winter apple tree varieties are suitable for cultivation in the Leningrad Region. The most popular include:

- In Memory of Lavrik;
- White filling;
- Melba;
- Delight;
- Antonovka;
- A gift to Grafsky.
If you don't have a large plot, the most suitable varieties for growing in the Leningrad Region are Vasyugan, President, and Medok. They can be easily planted even in areas with close groundwater levels.
Selecting a site for planting
To ensure your chosen seedling successfully establishes itself in the garden and produces a bountiful harvest, you should determine the most suitable site before transplanting it to its permanent location. Ideally, it should have the following characteristics:
- be located on a small hill;
- be illuminated by the sun's rays;
- be located outside of swampy areas, shade from buildings, drafts or mature trees;
- the soil acidity should be neutral;
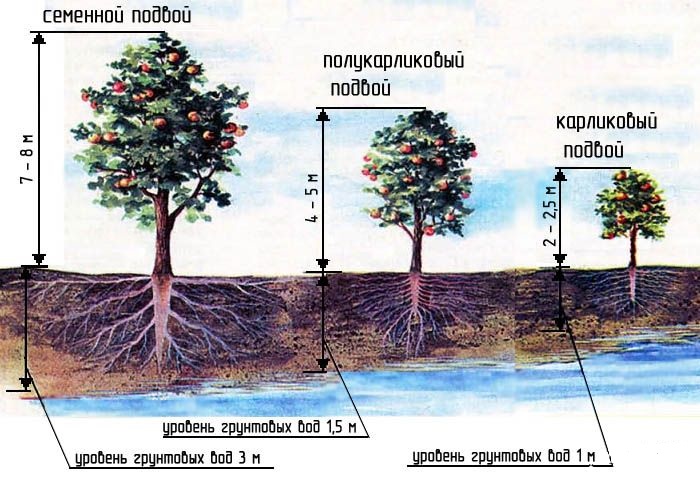
- groundwater must lie at a depth of at least 2 m.
If the selected site somehow does not meet the required conditions, its characteristics will have to be brought to an optimal state when planting the seedling.
Preparing for transplanting seedlings
Before planting a seedling, it must be carefully inspected. A plant that will thrive in its new location should have a healthy root system and a smooth trunk without any damage to the bark. Vibrant buds should be visible on a young plant. The day before transplanting, the seedling should be soaked in a bucket of water with a root growth stimulant.
It is recommended to use "Epin", "Kornevin", "Heteroauxin".
Preparing a hole for planting an apple tree
 When preparing the planting hole, pay special attention to its size and soil quality. Remember that apple trees prefer neutral soil. Before digging, remove all weeds and remove their roots. In summer, it's best to have rain the day before. Dig over the damp soil, and water the dry soil thoroughly to ensure it's thoroughly soaked. In spring, begin preparing the planting hole two weeks before the expected planting date. If you plan to plant the young tree in the fall, begin preparing the site six months in advance.
When preparing the planting hole, pay special attention to its size and soil quality. Remember that apple trees prefer neutral soil. Before digging, remove all weeds and remove their roots. In summer, it's best to have rain the day before. Dig over the damp soil, and water the dry soil thoroughly to ensure it's thoroughly soaked. In spring, begin preparing the planting hole two weeks before the expected planting date. If you plan to plant the young tree in the fall, begin preparing the site six months in advance.
The planting hole is surrounded by plastic film, with the top layer of soil from the hole placed on the right side and the deep soil on the left. The bottom is broken up with a crowbar or a bayonet shovel. Next, a nutrient mixture is prepared consisting of two buckets of organic matter (manure, compost, humus), 1 kg of nitroammophoska, and 0.8 kg of wood ash. Mix the soil mixture thoroughly. First, place the soil from the right side of the hole on the bottom, then add the nutrient mixture on top. This layer should be 20 cm above the top of the hole, as it will inevitably settle over time.
The size of the planting holes varies depending on the apple tree species. Tall varieties require holes at least 70 cm deep and up to 1 m in diameter, medium-sized trees require 70 x 80 cm, and dwarf varieties require 60 x 70 cm.
Landing
Immediately before planting, begin soil improvement. In sandy soils, add a drainage layer of dry clay and broken bricks, and deacidify peat soils with slaked lime, river sand, or dolomite flour.
In the spring, you will need to add 1 liter jar of wood ash to each hole.
Next, proceed as follows:
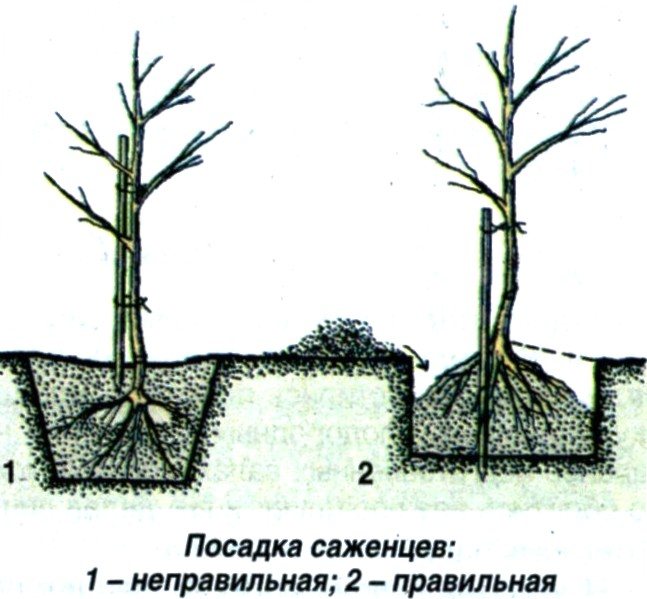
- Carefully remove the bag from the root ball, transfer the seedling to the prepared hole and fill it with fertile soil, compacting it.
- The grafting site should remain above the surface.
- Place a stake and tie the tree to it with a figure-eight loop.
- Water the seedling with 2 buckets of water, enclosing the trunk area with a border around the perimeter, at a distance of 50 cm from the center.
- Mulch the surface and pinch out the top.
Planting diagram
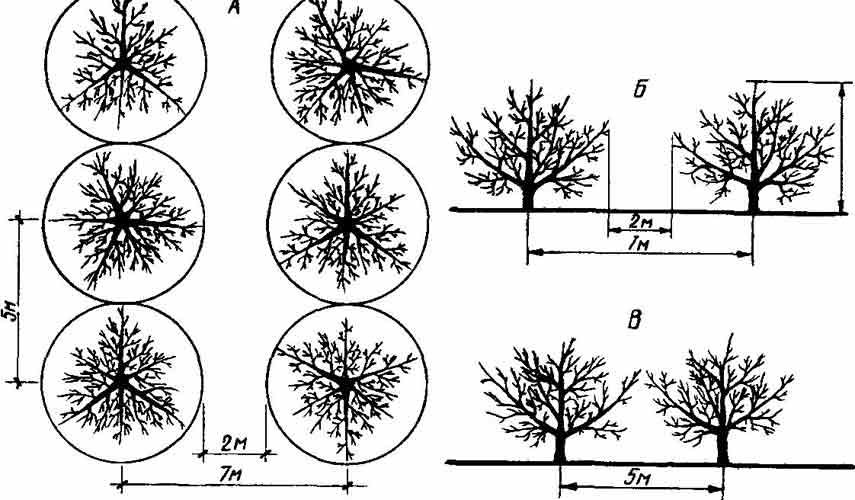
To ensure good tree growth and fruit production, it's important to consider several planting scheme considerations. Planting density is calculated based on the tree's biological characteristics. Vigorous apple varieties are planted at intervals of 4-6 meters, while shorter trees are spaced approximately 2 meters apart. Row spacing is maintained at 6-8 meters and 4-5 meters, respectively. Two apple trees on dwarf rootstocks should be planted at least 3 meters apart.
To extend the fruit harvest period, plant trees with different ripening times on the plot.
Care
After planting your apple tree, provide it with the care it deserves. To do this, keep the area clean, regularly perform sanitary and formative pruning, water the trees, and protect them from pests, frost, and disease.
Watering
The first month after planting the plant should be watered every weekAdd 2 buckets of water under each seedling. If the season is particularly dry, more frequent watering will be required – 2-3 buckets daily. Over time, reduce the frequency of watering, but increase the amount. Add 5 buckets of water under each plant once every 3 weeks.
A mature tree requires 4 glaze per season: the first – during the flowering period, the following ones – during the filling of the fruits.
Fertilizers
Provided that the hole has been prepared in advance, apply tree fertilizer will not be required for 2-3 years. Then, plants are fertilized as follows:
- Early spring fertilization is recommended to be carried out in the period from March 10 to April 15;
- in summer – in the first and second decades of June and, if necessary, in July;
- The first autumn feeding of apple trees occurs with August until September;
- the second – from September to October.
Organic fertilizers are considered the most valuable autumn fertilizers, as they contain all the essential nutrients apple trees require. They improve soil structure:
- make it looser;
- increase oxygen access to the root system;
- the soil composition improves.
Mineral fertilizers are used to supply the plant with one specific substance: phosphorus or potassium.
Trimming
In the Leningrad region pruning apple trees The season begins in mid-September and lasts until the end of October. Early and mid-season varieties are pruned in September – early October. Late varieties are pruned throughout October, after the leaves have fallen.
The first pruning of young trees is carried out immediately after planting them in a new location. If the tree has no lateral shoots, its top is shortened to form future scaffold branches. Pruning is performed as follows:
- For a branched one-year-old seedling, lateral shoots are removed up to 70 cm from the ground. If the branches are higher, only those that form an acute angle with the trunk are pruned.
- In the second year, the apple tree's skeleton is formed. Excess branches are removed, leaving 2-3 strong lateral branches. layeringThey are cut to 1/3 of their length.
- In the third year, the crown is thinned. Last year's branches are left, and new shoots are trimmed back by 1/3 of their length. Branches growing downwards and at a very sharp angle are removed.
- In the fourth year, all operations carried out in the third year of tree growth are repeated.
Graft
This procedure is carried out when the rootstock begins to match the scion's diameter. To do this:
- Select a smooth spot on the tree trunk that matches the diameter of the cutting.
- By moving towards yourself, make an oblique cut.
- Take the prepared cutting and apply the cut side to the prepared place so that the sections completely match.
- Wrap tightly with electrical tape.
Protection from diseases and pests
For apple trees growing in the Leningrad region, the most typical diseases are fruit rot And scabThey can be controlled by using fungicides or 3% Bordeaux mixture.
It is important to use a mixture of mineral fertilizers consisting of superphosphate, potassium chloride, ammonium nitrate and urea, diluted in water.
Preventive measures include regular pruning and care of the tree trunk area.
The most common pest is the green apple aphid. To get rid of it quickly, treat the trees with Ambush, Karbofos, or Actellic. Mealybugs are also common in the Leningrad Region; protection can be achieved by pruning affected branches and spraying with scale insecticides.
Conclusion
Growing apple trees in the Leningrad Region requires persistence and a smart approach. While achieving a good harvest isn't always easy, your efforts will definitely pay off.








