Quinti apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Reds |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Summer |
| Size of apples | Large |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Average tree height |
| Shelf life | Low shelf life |
| Application | For recycling , Fresh |
| Winter hardiness | Low winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | Up to 5 years |


 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
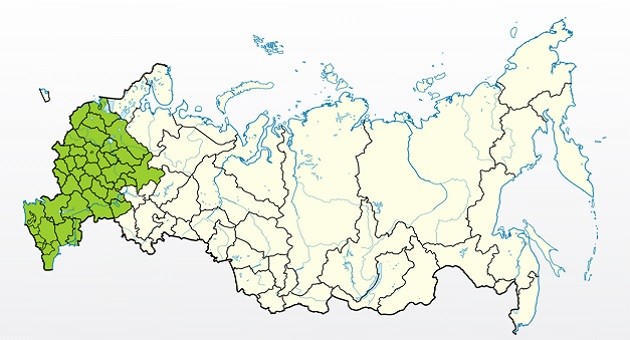
Growing regions
- European part of Russia.
- Moscow and Moscow region.
- North Caucasus.
- Northern regions (selective).
- Leningrad region.
- Crimea.
- Southern regions.
Origin
The development of this apple tree began around the 1960s in Canada. Two varieties previously well-known even in our country were used as parents: Melba Red and Crimson Beauty. In the late 1970s, the trees arrived in Europe and the Soviet Union. By 1971, Kvinti was accepted for state variety testing, which it passed with flying colors.
The apple tree was accepted into the State Register of Breeding Achievements in 1986. At the same time, it was officially zoned for the Lower Volga, North Caucasus, and Central Black Earth regions. In reality, it can be grown and bear fruit well in even larger areas.
Description of the Quinti variety
 Summer apple trees, which begin to delight gardeners with tasty, high-quality fruit early, have immediately caught the attention of many in our country. The trees are fairly compact, require little space, and begin bearing fruit early, delivering a bountiful harvest for many years without a rest period. They have moderate tolerance to low temperatures, are resistant to hot and dry summers, and rarely suffer from common apple tree diseases, particularly powdery mildew, although they can be severely and abundantly affected by scab.
Summer apple trees, which begin to delight gardeners with tasty, high-quality fruit early, have immediately caught the attention of many in our country. The trees are fairly compact, require little space, and begin bearing fruit early, delivering a bountiful harvest for many years without a rest period. They have moderate tolerance to low temperatures, are resistant to hot and dry summers, and rarely suffer from common apple tree diseases, particularly powdery mildew, although they can be severely and abundantly affected by scab.
Quinti apples are large, attractive, and have a very pleasant flavor, with a powerful, distinctive aroma. Although the fruit has virtually no shelf life and the trees are not particularly hardy in harsh Russian winters, they are recommended for both small private gardens and for commercial cultivation in intensive orchards, such as for juice, jam, and preserve production.
Apples: What do they look like?
 The fruits are medium-sized to large. With a small harvest or with flowering regulation, they can reach a weight of 200-240 grams, but under normal conditions, they reach approximately 165-190 grams. They are generally uniform in size, although a few apples may vary significantly in size, being round or slightly elongated, elongated, conical, or turnip-shaped, with a pointed tip toward the calyx. Ribbing is barely noticeable, and the lateral seam is completely invisible.
The fruits are medium-sized to large. With a small harvest or with flowering regulation, they can reach a weight of 200-240 grams, but under normal conditions, they reach approximately 165-190 grams. They are generally uniform in size, although a few apples may vary significantly in size, being round or slightly elongated, elongated, conical, or turnip-shaped, with a pointed tip toward the calyx. Ribbing is barely noticeable, and the lateral seam is completely invisible.
The skin is smooth and glossy, highly shiny, greenish-yellow or lemon-colored, and may sometimes acquire a waxy, oily coating when ripe. The blush is marbled, mottled, and diffuse, occupying 75-95% of the surface, almost obscuring the underlying color. It is red-orange, pinkish, or crimson, and can be visible on the dark side as stripes and specks ranging from lighter to darker. Subcutaneous punctures are numerous, very light and large, making them immediately visible. To assess the chemical composition, professionals recommend considering the following parameters:
- Sugar (fructose) – 11.1%.
- Pectins (fiber) – 15.6%.
- P-active substances – 234 milligrams.
- Titratable acids – 0.54%.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 11.7 grams.
The flesh is medium-dense, pleasantly firm, juicy, and coarse-grained. It has a distinct greenish hue, but by the time it's ripe for consumption, it acquires a creamy color. The flavor is considered dessert-like, balanced, harmonious, and sweet and sour. Experts praise it, giving it a tasting score of 4.6 out of 5.
Quinti apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 The trees are considered medium-sized, and some consider them to be natural semi-dwarfs, although they cannot truly be called compact. Quinti grows up to 4-5 meters without formative pruning, but most gardeners limit their growth to 3-3.5 meters.This makes garden maintenance and harvesting much easier. The crown is typically round or broadly oval, becoming spreading, drooping, and weeping over the years, with the tips of the long, thin, straight branches sometimes drooping to the ground. The bark is greenish-gray or brownish-gray, smooth, and pubescent. Fruiting occurs primarily on the previous year's ring shoots, less frequently on spears and fruiting twigs.
The trees are considered medium-sized, and some consider them to be natural semi-dwarfs, although they cannot truly be called compact. Quinti grows up to 4-5 meters without formative pruning, but most gardeners limit their growth to 3-3.5 meters.This makes garden maintenance and harvesting much easier. The crown is typically round or broadly oval, becoming spreading, drooping, and weeping over the years, with the tips of the long, thin, straight branches sometimes drooping to the ground. The bark is greenish-gray or brownish-gray, smooth, and pubescent. Fruiting occurs primarily on the previous year's ring shoots, less frequently on spears and fruiting twigs.
The leaves are thick, leathery, large, lanceolate, and equilateral, dark emerald, green, or simply emerald in color. They are flattened, long-pointed, with a serrated edge, which may be slightly wavy, but not significantly so, and may have a medium tomentose pubescence on the underside. The root system is medium to deep, branched, and fibrous, firmly anchoring the tree in the soil.
Productivity and pollination
The variety is officially classified as high-yielding, although it will hardly be able to keep up with such “masters” as Antonovka.
In one season, in favorable years due to weather conditions, thrifty owners harvest 110-130 kilograms of aromatic apples from a mature Quinti tree trunk..
Quinti is completely self-sterile, meaning it cannot serve as its own pollinator. Therefore, within 50-150 meters, it's essential to plant varieties with suitable flowering times to ensure cross-pollination. Advanced gardeners prefer to intersperse the trees, bring mobile apiaries to the garden during budding, and spray the trees with honey or sugar syrup.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
The variety's resistance to low temperatures is anything but exceptional. They struggle with temperatures barely reaching -22-25°C. However, with proper winter preparation and proper shelter, trees can be grown even in harsher conditions. The key is to properly insulate the trunks and rhizomes and limit autumn watering.
Apple trees are moderately susceptible to apple tree infections, which often plague Russian orchards. However, if there is no excess moisture and the area around the trunk is regularly cleared, they are rarely affected by powdery mildew. scab can attack them quickly and extensively. To prevent this, Quinti should receive timely, proper care and regular preventative treatment with fungicides and insecticides against insect pests.
Rootstocks and subspecies
Many different rootstocks are used to grow this variety, each of which can impart its own unique properties. However, there is also a subspecies of this variety, called Early Queen, recently developed in Holland. It is a winter variety, ripening around mid-October. Its fruits are larger, weighing 190-260 grams, and can be stored until mid-January or even longer.
Features of growing Quinti
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- Apple trees should be planted exclusively in sunny, open areas. However, care must be taken to ensure there are no drafts. In a strong wind, the seedlings will likely die while still young, while in the shade they grow weak and sometimes refuse to bloom.
- The variety is drought-resistant precisely because its roots penetrate deep into the soil, reaching for water. If the groundwater is too high, the shoots may rot and the trees will die. For the same reason, Quinti should not be planted directly near rivers, lakes, ponds, or even shallow wells.
- Preparing holes 6-8 months in advance isn't necessary for this variety, but it certainly won't hurt. Dig holes 60-80 centimeters deep and up to 1 meter in diameter, add fertilizer to the bottom, then drainage, and water with 35-45 liters of water. Leave the prepared holes uncovered.
- It's best to choose airy and fertile soil for planting, ensuring it allows water and air to pass through easily while still absorbing moisture. Sandy loam or clay soil should be fertilized, while black soil is best diluted with, for example, washed river sand to make it lighter.
- Leave a distance of up to 4-5 meters between trees, and even more between rows for ease of maintenance and harvesting. Moreover, the mature trees themselves will not clash with each other due to their crowns or rhizomes if they have ample space.
- Supports, such as wooden, metal, or plastic planks, are driven or dug into the holes, and the apple trees are tied to them after planting. If placed on the north side, they will not only serve as support, but will also protect from the cold.
- Root collar If you want to preserve the qualities and properties of the rootstock, apple trees should always be kept above ground level. Otherwise, the roots may grow higher, and all the properties will be lost.
- Place the seedling upright on a mound of soil or drainage material, spread the roots, cover with soil, and compact it by hand. Create a 10-15 cm high earthen bank around the perimeter of the hole, and pour 40-55 liters of water into it. It's advisable to mulch the surface.
Landing dates
In southern regions, where the weather is generally warm or moderate, Quinti can be planted in spring or fall. The trees root at roughly the same rate, with little difference. However, in areas where spring arrives later and winters are harsh and cold for the variety, it's best to plant early in the spring to allow the tree time to establish roots well and adapt to its new environment over the summer.
 Tree care
Tree care
Protection from frost and pests
In Crimea, the North Caucasus, and similar warm regions, trees can be wrapped using the standard method, simply wrapping the trunks with burlap, old tights, roofing felt, or tar paper. However, in colder climates, this will require more effort and time. You can pile spruce branches, straw bales, or dry grass mats around the roots. As a last resort, you can pile up a 15-20 centimeter layer of soil, which will need to be removed in the spring.
To protect Quinti from insect damage, you need to whiten Pruning trunks to a height of more than 1 metre twice a year – in spring and fall. If there's a risk of certain types of infestation, suitable insecticides from a gardening store can be used. Diseases can be prevented by regularly clearing the root zone of fallen leaves, especially fruit, eliminating unwanted excess moisture, and ensuring good crown ventilation. Regularly treating the trees with commercial fungicides is also helpful.
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Watering Young trees benefit from being fertilized once every 10-14 days. For mature trees, this frequency can be reduced to 6-7 times throughout the season, and only during particularly dry and hot periods. Fertilizer should be applied carefully to Quinti. For example, a fertilized hole at planting will last at least 2-3 years. Subsequently, it's important to monitor the tree's needs and fertilize it along with watering. Experienced gardeners recommend applying a tablespoon of ammonium nitrate diluted in 20-30 liters of water annually in the spring.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
The tree's dense foliage makes it appear densely planted, but this isn't entirely true. Crown shaping begins a year after planting in open ground. The central conductor is removed by a third, and the branches are shortened further, by five to seven centimeters. They should be planted in tiers, widely spaced, with two to four of the largest remaining.
In the future, all that remains is to maintain this sparse, tiered form by pruning away any unnecessary branches. For example, branches growing inward or upward should be removed. Dry, diseased, or damaged shoots should also be removed in the spring and fall. Rejuvenation can begin 12-15 years after the tree begins bearing fruit.
Pollinator varieties
- Champion.
- Gala.
- Currency.
- Melba.
- White filling.
- Everest.
Reproduction
- Grafting.
- Rooting.
- Growing from seeds.
Diseases and pests
- Powdery mildew.
- Scab.
- Green aphid.
- Fruit rot.
- Bacterial burn.
- Scale insect.
- Codling moth.
- Leaf roller.
- Hawthorn.
Ripening and fruiting of Quinti
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
This tree is very early maturing and begins bearing fruit as early as 2-3 years after planting in open ground. Sometimes you can see flowers in the first year, but it's best to pluck them immediately so the tree can develop roots and foliage first. The first harvests won't be abundant, yielding only 3-5 kilograms of aromatic fruit, but that's plenty for a sample.
Flowering time
Starting in mid-April, beautiful, large buds can be seen on the tree. They begin to open quite early, around the very beginning of May, or around mid-May in colder regions. They blossom into large, saucer-shaped, snow-white flowers, very delicate and fragrant, gathered in small inflorescences of 5-7. They densely cover the branches, and to ensure larger future fruits, advanced gardeners regulate the flowering period by picking 35-50% of the flowers evenly across the tree.
Fruiting and growth
Before fruiting, the tree can grow very quickly, gaining up to 50-60 centimeters per year, but then it slows down significantly. Therefore, you'll have to wait a long time for the tree to reach its maximum height of 12-15 centimeters per year. Yields also increase gradually, reaching their full potential only by the 15th to 18th year.
This apple tree blooms and produces fruit so quickly that it can produce two harvests in a single season under favorable conditions and warm weather. This phenomenon is widely reported in Crimea and the North Caucasus..
By mid-July, apples ripen on the tree and are ready for consumption. They are now perfectly suitable for eating fresh, making preserves, compotes, juices, jellies, and other delicacies. Unfortunately, preserving the fruit will only last for 7-10 days, after which they become limp, soft, tasteless, and begin to rot, even in the best cellar or refrigerator.
Top dressing
- Mineral complexes.
- Peat.
- Superphosphate.
- Compost.
- Manure.
- Chicken manure.
- Humus.
- Ammonium nitrate.
- Humus.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Inspect for diseases or pests.
- Organize timely regular watering.
- Fertilize.
- Transplant to a more suitable location.
Why do apples fall?
- Overripe.
- Natural weather disturbances.
- Pest damage.
- Various diseases.

Please share your own experience with the Quinti apple variety so that everyone can learn about it and avoid potential mistakes when growing their own garden.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting