Manchurian apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Reds |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Autumn |
| Size of apples | Small ones |
| Taste | Sour |
| Crown type | Tall tree |
| Shelf life | Low shelf life |
| Application | For recycling |
| Winter hardiness | High winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | From 5 years old |


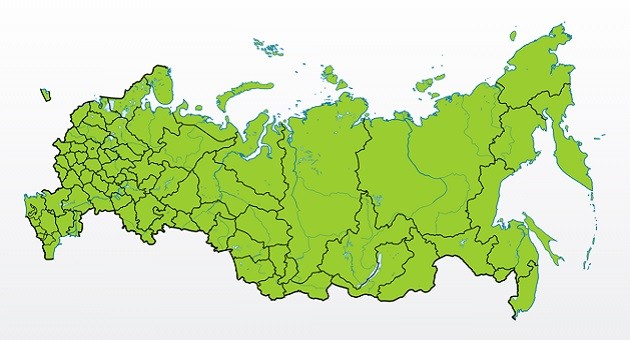 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
- Siberia.
- Moscow region.
- Crimea.
- Far East.
- North Caucasus.
- Leningrad region.
- Ural.
- Primorsky Krai.
- Northwestern regions.
- Middle zone.
Origin
This ancient apple tree, bred naturally, is listed in the Red Book and is rarely found in the wild today. It is believed to have descended from varieties native to northern China and Korea. Over the years, the variety spread to the Far East and Primorsky Krai. It is there that it can be found in protected areas, growing in clearings, forest edges, and as shrub thickets, alongside lilac, hawthorn, and ash.
Content
Description of the Manchurian variety
 This tree can be considered one of the tallest known. It has a dense, well-foliated crown and an unusually decorative appearance thanks to its long, knotty, and curved branches. The Manchurian apple tree enjoys abundant light, is undemanding in its growing conditions, requires little care, and is very tolerant of low temperatures.
This tree can be considered one of the tallest known. It has a dense, well-foliated crown and an unusually decorative appearance thanks to its long, knotty, and curved branches. The Manchurian apple tree enjoys abundant light, is undemanding in its growing conditions, requires little care, and is very tolerant of low temperatures.
The tree's fruits are small, but the flowers are beautiful, fragrant, and large. The tree is grown purely for ornamental purposes, so few people pay attention to the size and taste of the fruit. However, they can be added to various dishes, made into compotes, preserves, and jams. It is recommended for growing in private gardens as a landscaping element.
Apples: What do they look like?
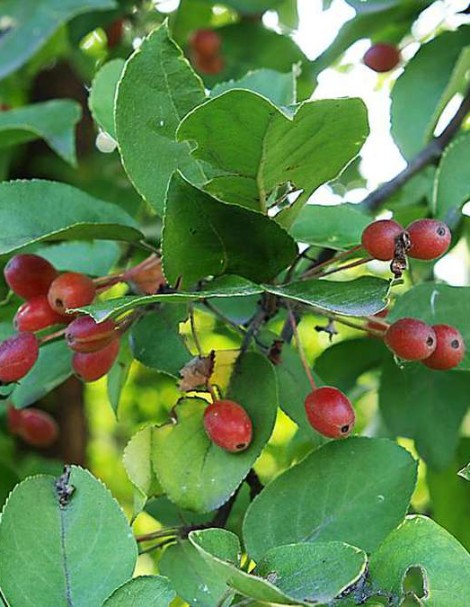
 The fruits of this variety are small to very small, barely reaching 1-1.4 centimeters in diameter. Their weight can range from approximately 3-6 grams. The shape is slightly elongated, cylindrical, and less commonly, spherical. They are smooth, with no noticeable ribbing and no lateral seam. The skin is dense, even firm, green or greenish-green. As it ripens, it turns yellow or golden, and may appear translucent or full-bodied. The blush is cherry red, red-orange, bright red, or carmine red.
The fruits of this variety are small to very small, barely reaching 1-1.4 centimeters in diameter. Their weight can range from approximately 3-6 grams. The shape is slightly elongated, cylindrical, and less commonly, spherical. They are smooth, with no noticeable ribbing and no lateral seam. The skin is dense, even firm, green or greenish-green. As it ripens, it turns yellow or golden, and may appear translucent or full-bodied. The blush is cherry red, red-orange, bright red, or carmine red.
The flesh is dense, grainy, and difficult to bite into. It's not very juicy, woody, but quite edible. The flavor is more sour, astringent, and bitter, with a slightly sweet aftertaste. After overripe, the consistency becomes softer, even spreadable. There's no official tasting rating for these apples. They're used for drying, making jams, compotes, and adding to meat and fish dishes.
Manchurian apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 A tall tree that can easily grow up to 10-14 meters, and sometimes even higherThe apple tree has a densely foliated, low-slung crown of a rounded or oval shape. With age, it becomes broadly oval, spreading, and drooping. The trunk is thick, with branches extending at right angles. They are long, geniculate, gnarled, curved, and rod-shaped, and can be smooth or pubescent, covered with bark that is reddish-brown, brown, or even cherry-colored. On the main stem, the bark is grayish-brown, almost black, and with age, it cracks and begins to fall off.
A tall tree that can easily grow up to 10-14 meters, and sometimes even higherThe apple tree has a densely foliated, low-slung crown of a rounded or oval shape. With age, it becomes broadly oval, spreading, and drooping. The trunk is thick, with branches extending at right angles. They are long, geniculate, gnarled, curved, and rod-shaped, and can be smooth or pubescent, covered with bark that is reddish-brown, brown, or even cherry-colored. On the main stem, the bark is grayish-brown, almost black, and with age, it cracks and begins to fall off.
The leaves are medium-sized or large, flattened, dense, and leathery, with a rough nervation. They are short-pointed, with a serrated-crenate edge, green or deep green in color. Young leaves are clearly pubescent on both sides, but by autumn, this pubescence only persists on the underside. The root system is usually taproot in the wild, deeply buried, branched, and extends 5-7 meters or more in diameter, adapted to seeking moisture in the soil.
Productivity and pollination
The Manchurian apple tree is considered a high-yielding fruit tree, but this is a relative statement. The harvest breaks all records in terms of fruit quantity, as the tree is literally covered in them in the fall. However, given their light weight, the resulting yield is limited in useful raw material for processing.
One adult tall tree trunk usually produces approximately 13-25 kilograms of very small fruits per year..
The variety is completely self-fertile, meaning it doesn't require any pollinators to bear fruit. Experienced gardeners say that harvests increase when other apple trees are within 50-60 meters, but few grow Manchurian apples for their fruiting. Therefore, it all depends on the intended purpose. However, a tree covered with hundreds of small, brightly colored apples against a backdrop of crystal-white snow looks very picturesque.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
This apple tree's resistance to low temperatures, sudden fluctuations and changes, and constant alternations between thaws and bitter frosts breaks almost all records. Like the Yagodnaya, it can easily be grown in the Far East, Siberia, and Primorsky Krai. With proper care, it can easily withstand temperatures down to -47-52°C. It is moderately drought-resistant and thrives in urban air pollution.
It has a moderate resistance to diseases. With regular preventative treatments, the risk of infection approaches zero. The apple tree is not afraid of either parasites or scabies, no powdery mildew if it is looked after properly and in a timely manner.
Rootstocks and subspecies
This apple tree is often referred to as a wild or semi-cultivated variety, and its subspecies are numerous and diverse. However, the main differences between the subspecies are the height of the trees, which can range from dwarf or creeping trees to enormous fifteen-meter-tall colossi. They also differ in the type of crown, which can be trained into bushes, hedges, freestanding trees, and more.
Features of growing Manchurian
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- A bright, open location is best for planting apple trees of this variety. They prefer good light and crown ventilation. However, they can also grow quite healthy in some shade, as long as they receive UV radiation for most of the day.
- Proximity to groundwater can be a serious problem for gardeners, as the Manchurian rhizome is deeply embedded. It easily reaches any moisture, only to begin rotting. For this reason, avoid planting this variety near rivers, lakes, ponds, or even shallow wells. If you have no other options, it's best to plant trees on slopes, hills, or artificial embankments, after creating a makeshift root barrier—burying a sheet of slate or several layers of roofing felt or tar paper at a depth of 2-3 meters.
- Preparing the holes in advance is possible, but not necessary. It's best to do them at least 2-3 weeks in advance. Dig holes 80-90 centimeters deep and up to 1-1.2 meters in diameter. Add fertilizer to the bottom, a 10-15 centimeter layer of fertile soil or drainage on top, and fill with water (35-40 liters). The holes should be left outdoors without covering them.
- Stakes or planks for tying the tree up are driven in (dug in) immediately; in some cases, it's worthwhile to create entire racks. More than one young tree can be tied to these. The structure will provide not only support but also protection from the cold northern winds in the harshest regions. These supports should not be removed until the apple tree's third year.
- Root collar It's customary to leave the collar above the soil surface, taking into account its subsidence after the first waterings. It should be calculated so that the soil will settle by at least 2-4 centimeters, therefore the collar should protrude by 5-8.
- Leave about 5-6 meters between trees, unless you're creating a shrub-type hedge or a living space. Manchurian rhizomes are very tall, and their rhizomes grow even more extensively. Therefore, space rows up to 6-8 meters apart; this placement also simplifies maintenance. For smaller trees, 3-4 meters is sufficient, and sometimes even less. Shrubs for fencing and decorative purposes can be placed close to other plants or garden structures, such as gazebos, benches, pergolas, etc.
- Place the seedling on a drainage layer or a pile of soil, spread the rhizome out so it lies loosely, cover with soil, and compact it by hand. Water with 35-45 liters of water, and the surface mulch, if moisture retention is required.
Landing dates
In northern regions with harsh climates, where Manchurian apple is most commonly grown, it's best to plant it in early spring, before the sap begins to flow. Over the summer, the apple tree will have time to adapt to the new conditions, strengthen, and establish roots, making it easier to survive its first winter. In warmer, more moderate climates, trees can be planted in the fall, after the leaves have fallen, but keep in mind that the first frost should be at least 2-3 weeks away.
 Tree care
Tree care
Protection from frost and pests
Young trees require standard protection: covering the root zone with bales of straw or hay, spruce branches, and even soil, wrapping the trunks with burlap, roofing felt, or roofing felt, and insulating with agrofibre. In the coldest regions, young saplings are covered with a tent-like covering, but this is not suitable for mature trees.
To remove insects that nest in bark crevices, whitewash the trunk with lime twice a year, in the fall and spring. Coating the trunk with lard, tallow, fuel oil, or grease will help repel rodents. Regularly spray the trees with commercial fungicides and insecticides.
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Around young apple trees, it's customary to dig the soil once or twice a year, as needed. At the same time, remove root suckers, weeds, and shoots from other trees and shrubs. In between, you can hoe the soil, loosening it, for example, the day after glazeOver the years, the need for regular loosening disappears, so the area around the trunk can be covered with sod or seeded with lawn grass.
Apple trees require virtually no watering if the weather is normal. Additional water may be necessary only during severe drought and heat, when precipitation has not fallen for more than 3-4 weeks and temperatures are excessively high. Along with water, you can apply fertilizers and supplements, which trees rarely require. If desired, you can set up sprinkler or drip irrigation. watering, but even without such tricks they grow well.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
This tree is so flexible that it can be molded into almost any shape imaginable. Apple trees are used to form hedges and create all sorts of unusual bushes, but they can also be grown as a simple, sparsely layered tree.
All dead or diseased shoots should be removed regularly. Broken shoots should also not be left behind; it's best to cut them off immediately. All cut areas should be sealed with mulch, water-based paint, or garden pitch.
Pollinator varieties
- Gorno-Altaisk.
- Altai ruddy.
- Haste.
- Sakhalin pendula.
- Abundantly flowering.
- Firebird.
- Ranetka.
- Nastenka.
Reproduction
- Grafting by cuttings.
- Growing from seeds.
- Rooting cuttings.
Diseases and pests
- Cytosporosis.
- Green aphid.
- Bacterial burn.
- Scale insect.
- Leaf roller.
- Scale insect.
Ripening and fruiting of Manchurian
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
Apple trees begin bearing fruit quite late, approximately 10-11 years after planting in open ground. Therefore, they can hardly be called early fruiting. However, yields reach their maximum within just a few years, although these trees are rarely planted for apple production.
Flowering time
This factor largely depends on the growing location. For example, in Primorsky Krai, it most often blooms only in late May, while in the Moscow region it can bloom as early as the beginning of the month. In the former case, the flowering period may be 5-7 days longer. On average, Manchurian lily blooms for 16-20 days, allowing everyone to fully enjoy its beautiful appearance and fragrance. The flowers grow densely, are large, snow-white or with pink centers and delicate petals, gathered in umbel-shaped inflorescences of 5-8.
Fruiting and growth
The tree grows at a moderate rate, gaining only 15-25 centimeters per year. However, its yield increases rapidly, reaching its peak by the 14th or 15th year. Another issue is that Manchurian figs are rarely grown for harvesting.
Small red apples begin to ripen in mid- to late September in northern regions. In warmer climates, they may ripen earlier, but it's customary not to rush to pick them. These fruits don't fall from the branches until spring, so they can be picked at any time. Some simply leave the fruit on the tree to add a picturesque appearance to the garden during winter. These apples can't be stored in a cellar; their shelf life is a maximum of one month.
Top dressing
- Peat.
- Compost.
- Manure.
- Chicken manure.
- Humus.
- Superphosphate.
- Humus.
- Ammonium nitrate.
- Dolomite flour.
- Wood ash.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Inspect for diseases or pests.
- Limit watering.
- Fertilize.
- Transplant to another location.
Why do apples fall?
- Natural weather conditions (wind, rain, hurricane, hail).
- Pest damage.
- Various diseases.
Share your own experience with the Manchurian apple variety so everyone can experience it and enjoy it as a wonderful addition to their garden or a piquant addition to juices or jams.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting






