Chinese Golden Apple Tree: Variety Features and Care
| Color | Yellow |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Autumn |
| Size of apples | Small ones |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Tall tree , Average tree height |
| Shelf life | Low shelf life |
| Application | For recycling , Ornamental tree |
| Winter hardiness | High winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | Up to 5 years |


 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
The variety has its own regional distribution: the Volga-Vyatka and North-West regions, where it is included in the State Register.
Origin
The renowned Russian biologist and breeder Vladimir Ivanovich Michurin was the first to turn his attention to small-fruited apple trees in the context of domestic breeding in the late nineteenth century. Through a variety of crosses, he also succeeded in producing the Golden Kitayka, which we are interested in today, the "ancestors" of which are the White Naliv and the common Kitayka (Plum-leaved, Paradise apple).
Over time, many varieties of Kitayka spread throughout the country, and then around the world. It was primarily planted for its unusual clusters of small apples and its relatively high frost resistance.
Content
Description of the Chinese Golden Apple tree variety
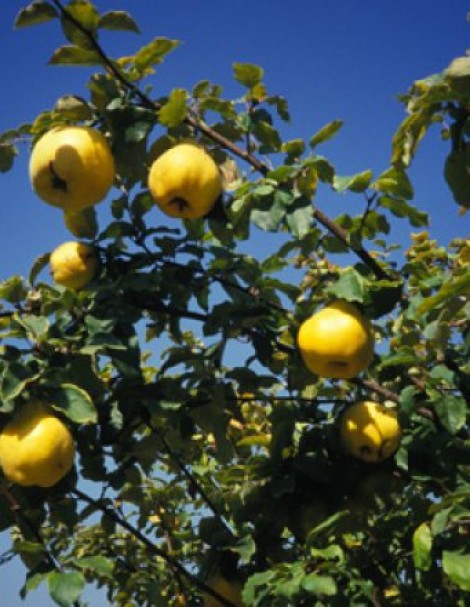
 This old Michurin apple variety is grown not only for harvesting, although its fruits are tasty and aromatic, but also for ornamental purposes. It is distinguished by its high tolerance to low temperatures, which is why it is widespread in various regions of our country, and also by its early fruiting. Commercial cultivation of the Golden Kitayka is not common, as its shelf life leaves much to be desired.
This old Michurin apple variety is grown not only for harvesting, although its fruits are tasty and aromatic, but also for ornamental purposes. It is distinguished by its high tolerance to low temperatures, which is why it is widespread in various regions of our country, and also by its early fruiting. Commercial cultivation of the Golden Kitayka is not common, as its shelf life leaves much to be desired.
Apples: color, size, weight
 The fruits of this tree are quite small, weighing no more than 30-50 grams even for the largest varieties. Initially, the apples have a greenish or light green hue, but as they ripen, they turn golden yellow, hence their name. Their skin is thin and easily damaged. Therefore, these apples are completely unsuitable for transportation. When fully ripe, they "fill out," becoming translucent; when held up to the light, you can even see the seed pods inside. The chemical composition per 100 grams of the product is characterized by the following substances:
The fruits of this tree are quite small, weighing no more than 30-50 grams even for the largest varieties. Initially, the apples have a greenish or light green hue, but as they ripen, they turn golden yellow, hence their name. Their skin is thin and easily damaged. Therefore, these apples are completely unsuitable for transportation. When fully ripe, they "fill out," becoming translucent; when held up to the light, you can even see the seed pods inside. The chemical composition per 100 grams of the product is characterized by the following substances:
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 17.7-17.9 milligrams.
- Total sugars (fructose) – 18.8%.
- P-active substances – 162 milligrams.
- Pectins (fiber) – 11-12%.
- Acidity – 2.91%.
- Polyphenols – 0.88%.
The fruits don't hold well on the branches, quickly falling off when overripe or shaken (by wind or rain). Their flesh is very tender, juicy, and quite sweet, but with a distinct, characteristic tartness. It's white or translucent white in color. There's no official tasting rating for these apples.
Chinese Golden Apple Tree: Characteristics
Crown and root system
 It is believed that the Chinese golden tree is a medium-sized tree, although under favorable conditions it can easily reach a height of 6-7 meters. However, gardeners usually use pruning to shape the crown so that it doesn't grow beyond 3-4 meters. At an early age crown It has a distinct broom-like shape, with branches extending from the main trunk at an acute angle. Over time, it becomes spreading, almost weeping, and can cover an area up to 4-6 meters in diameter.
It is believed that the Chinese golden tree is a medium-sized tree, although under favorable conditions it can easily reach a height of 6-7 meters. However, gardeners usually use pruning to shape the crown so that it doesn't grow beyond 3-4 meters. At an early age crown It has a distinct broom-like shape, with branches extending from the main trunk at an acute angle. Over time, it becomes spreading, almost weeping, and can cover an area up to 4-6 meters in diameter.
The bark on young shoots is light green, but with age it becomes rougher, becoming grayish or brown, and becoming cracked and rough. The leaves are large, elongated, pointed, with jagged edges, light green, and lack the characteristic leathery sheen. The root system depends entirely on the rootstock, but is generally superficial and branched.
Productivity and pollination
The Chinese Golden Apple is not self-fertile, so without nearby pollinators, no fruit will be produced. Therefore, varieties with suitable flowering times should be planted no more than 150-200 meters away. Furthermore, it can act as a pollinator itself.
The problem is the fruit falling off as it ripens, which is best picked as early as possible. As soon as they start to rot even slightly, they immediately fall to the ground.
This drought- and frost-hardy tree begins bearing fruit as early as 2-3 years after planting. It doesn't reach full fruiting until 5-8 years. However, large yields are not expected due to the small size of the apples. The tree is considered to have a very long lifespan, and can produce fruit even in its seventieth year.
No more than 25-50 kilograms of fruit can be harvested from one tree.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
This Chinese variety has a fairly high tolerance to low temperatures, but it struggles to withstand temperatures below -40°C. Therefore, it is common in many regions, except for the Far East and SiberiaIn this case, the tree may not die completely, but it may suffer severely.
The tree will have to be carefully looked after, because it has no immunity to scab or other apple diseases.
Subspecies and rootstocks
Subspecies
| Subspecies | Description |
| Decorative | This subspecies doesn't require formative pruning, as its crown isn't overly dense. It has elliptical leaves that are pointed and elongated. It blooms with large, bright pink flowers that are intensely fragrant, and produces small yellow apples with a tart-sweet flavor. |
| Early | An early-ripening subspecies that is very drought-resistant. It lacks the high frost resistance of other varieties and is especially common in the central and eastern regions. The apples ripen faster than many early varieties and can be picked as early as mid-July. They don't keep for long, so they should be eaten or processed no later than 5-7 days after harvest. |
| Late | This variety of Kitayka is not only drought-resistant but also resistant to severe frosts. It begins bearing fruit slightly later than other varieties, only in the fourth to sixth year, but this is more than compensated for by the fact that the apples are less susceptible to rapid shedding. |
| Large-fruited | A low-growing tree that tolerates low temperatures well. It has a mid-season fruiting and ripening period. It produces larger fruits, up to 60-80 grams, in large quantities. It grows in various regions, including Siberia and the Far East. |
Rootstocks: features
Chinese goldenrod can be grafted onto a wide variety of rootstocks, which can ultimately produce completely different results.
| Rootstocks | Peculiarities |
| Dwarf | This is the most common option, which ultimately allows the tree to grow up to 2 meters in height, which significantly increases its decorative qualities and also simplifies harvesting. |
| Semi-dwarf | It grows to an average height of 3-4 meters. Typically, rapid growth is observed in the first few years, which slows significantly once the first fruits appear. |
| Creeping | This is a truly remarkable rootstock, allowing apple trees to be grown even in the harshest conditions of the Far North. It's considered a summer variety, ripening no later than August. Its ground-hugging branches make it easy to protect from winter frosts. The fruits of these Chinese apple trees are larger, slightly tart, and have a powerful aroma. |
| Columnar | On this rootstock, the tree grows early and is more ornamental than fruit-bearing. It reaches a height of no more than 2-2.5 meters, has almost no lateral scaffold branches, and the apples are attached in clusters directly to the central trunk. |
Features of growing Chinese golden
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- Choose locations where the groundwater level is no higher than three meters below the surface. Avoid planting in low-lying areas or near open water, as frequent standing water can damage the root system.
- The holes for apple trees are dug 80-85 centimeters deep and 1 meter in diameter.
- If the roots of the seedlings have dried out during transportation, it's best to moisten them first. To do this, place each one individually in a bucket of water. Damaged roots can be trimmed with pruning shears if necessary.
- At the bottom of the hole, pour soil mixed with leaf humus and a small amount of manure, preferably horse manure.
- Place the seedlings so that the root collar protrudes 3-5 centimeters above the surface.
- Immediately dig in the stakes, preferably on the north side.
- Cover the seedlings with soil, shaking them gently to remove air pockets around the rhizomes. Don't compact the soil around them; a gentle press is sufficient.
- Trees are planted quite close to each other, 2-3 meters is enough.
Apple trees of the Kitayka Zolotaya variety require special soils, preferably loamy or sandy loam.
Landing dates
In order for the Chinese cabbage to take root better, it should be planted in the spring, in early or mid-April, before the buds begin to open.
Protection from frost and rodents
The variety is considered winter-hardy, but it should still be protected from severe frosts initially. This will ensure survival, and it will also allow the first apples to be seen as early as the second year after planting the seedling in open ground.
To achieve this, the trunks are mulched with horse manure in the fall. They are usually insulated with spruce branches, burlap, straw, and even ordinary nylon tights. It's a good idea to first whitewash the trunks with lime, treat them with lard, or grease to protect them from rodents.
 Tree care
Tree care
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
The soil for the Golden Chinese Cactus needs to be loosened regularly, which is best accomplished by digging around the tree's trunk in spring and fall. It's also a good idea to remove weeds, rake up fallen leaves, and remove fallen fruit from under the tree.
This variety almost never requires watering, as it is highly drought-tolerant. Even in the hottest summers, the tree draws moisture from the soil itself. It is usually watered only when fertilizing.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
This variety doesn't require early formative pruning due to its panicle growth habit. After 3-4 years of growth, this can be addressed in the spring. To ensure proper pruning, simply select a few of the strongest, largest branches that you want to develop, and trim the remaining branches with pruning shears.
Sanitary pruning should be done regularly. This involves removing all old, dried, diseased, or damaged branches in the fall. Maintenance pruning is avoided, as the small fruits don't put much strain on the branches.
Most often, Chinese Golden Apple is grafted onto suitable apple and pear varieties. However, the latter option is not very desirable, as it significantly reduces the frost resistance for which the variety is so prized.
Pollinator varieties
- Folder.
- White filling.
- Grushovka.
Reproduction
- Layers (clones).
- Growing from seeds.
- Grafting (rootstock) by buds or cuttings.
Diseases and pests
- Scab.
- Powdery mildew.
- Cytosporosis.
- White coating.
- Codling moth.
- Green aphid.
Of particular danger to the Chinese is mushroomA tinder fungus that, as it grows, sucks all the juices out of a fruit tree. If its presence isn't noticed and eliminated in time, the apple tree will likely die. However, even if you manage to save it, fruit production will drop significantly. Therefore, the fungus must be cut off immediately, before it has time to harden, and the cut area must be covered with oil paint.
Ripening and fruiting of the Golden Kitayka apple tree
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
The Chinese Golden Apple is considered an early-bearing apple tree, with the first fruits appearing on the tree in the second or third year. The longest wait for fruiting occurs with the late-ripening subspecies, which only matures four or five years after planting in open ground.
Flowering time
Early varieties of Chinese orchids typically bloom as early as late April, but more often this occurs in early to mid-May. They are literally covered in beautiful, large pink flowers.
Fruiting and growth
The fruits ripen as early as mid-July. It's crucial to be on time for harvesting. Within a week, all the fruits will likely have fallen to the ground and will need to be processed immediately.
On average, even a particularly fruitful apple tree yields no more than 35-50 kilograms of apples, and even then, only in a good year. The fruit is completely unstorable, and after a week, its flavor deteriorates significantly, and it begins to rot very quickly. Maximum fruiting can be expected between the 5th and 8th years of life.
Top dressing
- Leaf humus.
- Manure (preferably horse).
- Nitrogen fertilizers.
- Urea.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Check for diseases or pests.
- Prune old, diseased or damaged branches.
- Check for stagnant water near the rhizome.
- Transplant to a more fertile area.
Why do apples fall?
- Natural phenomena.
- Excess moisture.
- Pests.
- Diseases.

Leave your feedback on the Golden Chinese Cactus in the comments to see what other gardeners think of your experience.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting








Comments
The Kitayka Zolotaya variety stands out among its apple peers. Its flavor is a combination of peach or pineapple with apple. It bears fruit regularly and is treated with solutions every season. I removed the polypore fungus early on. This delicious variety requires careful care.