Aborigen apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Reds |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Summer |
| Size of apples | Small ones |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Average tree height |
| Shelf life | Low shelf life |
| Application | Fresh , For recycling |
| Winter hardiness | High winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | Up to 5 years |


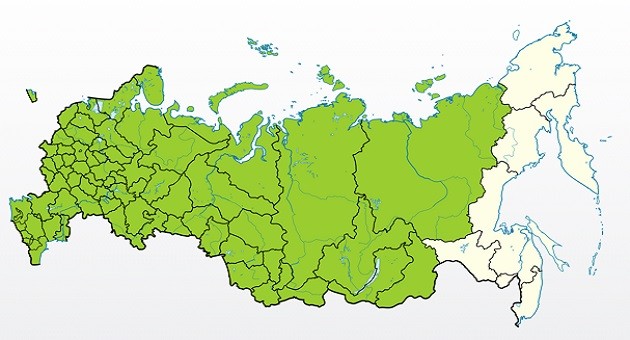 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
- Leningrad region.
- Siberia.
- Far East.
- Middle zone.
- Moscow region.
- Northern regions.
- Ural.
Origin
The new winter-hardy hybrid was developed by Russian-Soviet scientist Alexei Vasilyevich Bolonyaev at the experimental station of the Far Eastern Research Institute of Agriculture in the late 1960s. The already well-known Rebristoye, Tochnoye, and Avgustovskoye Dalnevostochnoye varieties were used as parent varieties.
In 1970, an application for registration was submitted following highly successful trials at a farm in Khabarovsk Krai. Four years later, the application was approved, and Aborigen was included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements and zoned for the Far East.
Content
Description of the Aborigen variety
 Compared to other northern apple trees, this variety produces fairly large and attractive fruits. They are tasty and have high marketable qualities, although they don't keep well. The trees are quite compact, allowing for large harvests from a small area.
Compared to other northern apple trees, this variety produces fairly large and attractive fruits. They are tasty and have high marketable qualities, although they don't keep well. The trees are quite compact, allowing for large harvests from a small area.
They are resistant to low temperatures, bacterial and fungal infections, undemanding of growing conditions, easily withstand summer heat, and produce fruit during a short warm period. Recommended for planting in large commercial and intensive gardens, as well as for small backyards.
Apples: What do they look like?
 The fruits of the Aborigen variety are small to very small. They reach a maximum weight of 120-140 grams, but only on individual branches in favorable years. The bulk of the fruit barely reaches 45-60 grams. The fruit is round, spherical, smooth, and can be slightly elongated, with virtually no ribbing.
The fruits of the Aborigen variety are small to very small. They reach a maximum weight of 120-140 grams, but only on individual branches in favorable years. The bulk of the fruit barely reaches 45-60 grams. The fruit is round, spherical, smooth, and can be slightly elongated, with virtually no ribbing.
The skin is smooth and shiny, dense, bordering on hard, brittle yet moderately elastic, and provides good protection against mechanical damage. It is green, becoming increasingly whitish-yellow and golden as it ripens. The blush is quite intense, red or carmine-red, striped and streaked, typically covering approximately 45-65% of the surface, and is more intense on the sunny side. Subcutaneous dots are large, light green, may be slightly grayish, clearly visible, and numerous. Distinctive chemical characteristics are as follows:
- P-active substances – 242 milligrams.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 4 grams.
- Sugar (fructose) – 11.7%.
- Titratable acids – 0.75%.
- Pectins (fiber) – 0.5%.
The apple flesh is medium-dense, fresh, crisp, fine-grained, and very juicy. It has a pleasant, sometimes slightly astringent, sweet flavor with a tart aftertaste and a memorable, powerful, distinctive aroma. Professional tasters rate the fruit 4.5-4.6 points for taste and appearance, respectively.
Aborigen apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 This tree is generally considered medium-sized, although a more logical term would be a natural semi-dwarf. It can grow to a maximum height of 3.3-3.7 meters in its lifetime and rarely reaches 4-4.5 meters. Gardeners prefer to limit pruning to 2.5-3 meters, which provides certain advantages in care and harvesting. The crown is spherical or rounded-elongated, with long, thick, straight branches arranged at an angle close to right angles. They are covered with gray-brown bark with a slight metallic sheen.
This tree is generally considered medium-sized, although a more logical term would be a natural semi-dwarf. It can grow to a maximum height of 3.3-3.7 meters in its lifetime and rarely reaches 4-4.5 meters. Gardeners prefer to limit pruning to 2.5-3 meters, which provides certain advantages in care and harvesting. The crown is spherical or rounded-elongated, with long, thick, straight branches arranged at an angle close to right angles. They are covered with gray-brown bark with a slight metallic sheen.
The leaves are fairly dense, large, slightly wrinkled, and light green or deep green. They are dense and leathery, with rough nervation, a long-pointed tip, and serrated, serrated, and sometimes slightly wavy margins. The underside of the leaf blade is usually heavily pubescent. The root system, depending on the rootstock, can be fibrous and highly branched, or taproot, deeply rooted, adapted to seeking moisture deep within the soil.
Productivity and pollination
For a small tree, the number of fruits ripening on the branches can be called abundant, and the tree itself is highly productive.
The Aborigen variety's fruitfulness increases gradually. It's minimal in the first few years, but a ten-year-old tree will produce over 55-65 kilograms of tasty, aromatic, albeit small, apples. Its key characteristic is its continuous annual fruiting from the beginning to the end of its lifespan, without any rest periods.
The variety is conditionally self-fertile, so you'll definitely get some fruit even if there's not a single apple tree within 45-100 meters. However, to maximize fruit production, pollinators in the form of suitable varieties are essential. To more actively attract bees, experienced growers spray the garden with sugar or honey syrup during bud break and move hives closer to the plantings.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
The aborigine is extremely frost-resistant, as it was bred specifically to allow people to grow it in the harsh conditions of northern Russia. It can withstand temperatures down to -42-45°C if the trees are properly winterized and covered. It can tolerate less severe frosts even without special protection, but only if they last no longer than 2-4 weeks at a time. It dislikes sudden changes and fluctuations in temperature and does not tolerate drafts.
Apple trees are resistant to moniliosis, scab, powdery mildew, and other fungal infections. They rarely become infected, and even when they do, the damage is minor. Typically, only the leaves are affected, while the fruit can be eaten or processed. However, regular preventative treatments against diseases and pests are a good idea.
Rootstocks and subspecies
This variety has no subspecies, but Aborigen can be grown on various rootstocks. It can also serve as a good winter-hardy base for virtually any variety. The rootstock used can directly affect the fruit size and frost resistance of the trees. Dwarf and semi-dwarf varieties produce larger fruits, but have lower winter hardiness. Creeping varieties can produce apple trees that can withstand the harshest winters.
Features of growing Aborigen
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- It's best to choose a site for an apple tree where the groundwater level is deeper than 2.4-2.6 meters. The tree's roots can reach the water and begin to rot, which usually leads to rot.
- A sunny, open location is a good option for the Aborigen, but it will also grow successfully in the shade. However, its yield may be somewhat reduced; the fruits are smaller and not as juicy and sweet.
- The crowns need good ventilation, and the roots need space and nutrients, so it's not recommended to plant apple trees too close together. The optimal distance between tree trunks is 3-4 meters, with the same distance between rows.
- The tree grows well in almost any soil, as long as its pH doesn't exceed 6-6.5, otherwise it may die. If the soil is too acidic, you can reduce the acidity with lime beforehand or add chalk or dolomite powder mixed with washed river sand at planting.
- Planting holes are prepared a season in advance, but if the time is missed, they can be dug 3-4 weeks in advance, allowing them to sit outdoors for at least that long. To do this, dig holes 80 centimeters deep and up to a meter in diameter, make steep sides, and fill the bottom with soil mixed with fertilizer. Drainage is added if needed, and the bottom is filled with water (35-50 liters).
- Before planting, the tree is inspected, all broken or dried roots are cut off, and the tree is immersed in water for 6-8 hours so that the apple tree is saturated with moisture.
- Place the tree vertically so that root collar rises 6-9 centimeters above the surface. Otherwise, the properties and qualities of the rootstock will be lost.
- Cover the tree with soil, compacting it layer by layer with your hands, leaving no air pockets. Water with 35-40 liters of water, and mulch the surface. This can be done with chopped grass, sawdust, compost, or manure.
Landing dates
These Far Eastern apple trees thrive best when planted in the spring. This makes it much easier to determine the right time. Ideally, it should be a warm spring day in late March or early April, when the soil has warmed up well and the threat of frost has passed. In warmer climates, Aborigen can also be planted in the fall, but make sure there are at least 4-5 weeks before frost and the leaves have already fallen.
 Tree care
Tree care
Protection from frost and pests
All standard frost protection measures for trunks are carried out regularly and promptly to preserve the garden and ensure good harvests every year. First, watering is reduced starting in August, and by September, no water is applied at all. The trunks are wrapped in burlap, and the root zone is covered with spruce branches, straw bundles, hay mats, and bundles of well-dried leaves. Creeping trees can even be covered with soil, while all other varieties should be wrapped like a tent.
Whiten It's no coincidence that it's common practice to lime tree trunks in spring and fall; this drives away pesky insects from the cracks in the bark and the spaces between the roots. To drive away haresTo prevent mice, hamsters and other rodents that feast on the tender bark and shoots, apply melted lard, fuel oil, grease, old oil or drying oil to the trunks.
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Dig up the root zone around the tree once a year; that's enough. Once the trunk grows, you can sow it with herbs or cover it with sod, eliminating the need to remove weeds or loosen the soil. Initially, it's a good idea to hoe the soil 2-4 times a season to allow oxygen to reach the roots.
Aborigen requires almost no watering, as its rhizomes are often able to penetrate deep in search of moisture. Optimally, watering should be done 3-4 times per season, and only in hot and dry years. This can be timed to coincide with the beginning of flowering, fruit set, and apple ripening. At this time, you can apply fertilizers and fertilizers that are better absorbed by water.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
You can begin pruning a tree in its first year if it is strong, with a thick trunk and well-developed branches. If the sapling is weak, it's best to postpone the process until the second year. Prune the central basal conductor, as well as the main skeletal branches, to 2-3 buds. However, remember not to remove more than two-thirds of the tree's foliage at a time, as this can cause severe disease. The trunk should always remain at least 4-7 centimeters longer than the branches.
Dry, diseased shoots are also removed, as they will only draw sap in vain, growing inwards to the crown and thickening it, and sticking upwards. spinning topsRejuvenation is usually not carried out, since the lifespan of the native is not very long, only 45-50 years, but in the 7-9 year, you can begin to cut off 1-2 age branches, repeating the action after 2-3 years.
Pollinator varieties
- Amur red.
- Reliable.
- Avant-garde.
- Augustovskoye Far Eastern.
- Ranets.
- Amur filling.
Reproduction
- Rooting.
- Kidney grafting.
- Growing from seeds.
- Cuttings.
Diseases and pests
- Black crayfish.
- Scab.
- Bacterial burn.
- Powdery mildew.
- Green aphid.
- Codling moth.
- Leaf roller.
- Hawthorn.
Ripening and fruiting of the Aborigen
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
This variety is considered early-bearing. The first fruits can be harvested as early as 3-5 years. The harvest will be impressive right away, weighing approximately 7-9 kilograms with good care and favorable weather and climate conditions. To increase the size of the fruit in subsequent years, thinning the buds is recommended.
Flowering time
The Aborigen begins to bloom in May. This can occur in mid-June, late June, or even early June. This all depends on the weather and region of the previous winter, including how cold and snowy it was. The process lasts approximately two weeks, during which time the bees always have time to complete their pollination work. The flowers are large, saucer-shaped, with fleshy pink petals that are very delicate in appearance. They are arranged in clusters of 5-6 on the branches and have a strong and pleasant scent.
Fruiting and growth
The Aborigen tree is capable of rapidly accelerating its growth and fruiting. Within 4-5 years of fruiting, it reaches its full natural height and yield. The tree grows approximately 55-70 centimeters per year, which is significant, especially in the early stages. At this point, a single tree can yield at least 50-60 kilograms of aromatic fruit.
This apple tree has a diverse set of chromosomes from various parent varieties, hence its nickname, a chimera. All such apples ripen very early, as early as mid-August or at the end of the month. However, on some branches, they may linger and ripen several weeks later. When overripe, the fruits drop, so you'll need to monitor them closely. Their shelf life is short, only 25-40 days in good conditions, so it's best to eat them immediately or process them.
Top dressing
- Peat.
- Compost.
- Ammonium nitrate.
- Humus.
- Chicken manure.
- Superphosphate.
- Manure.
- Mineral complexes.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Check for pests or diseases.
- Transplant into the sun.
- Water.
- Fertilize.
Why do apples fall?
- Wind, hail, hurricane, rain.
- Pest damage.
- Diseases.

Please leave your feedback on the Aborigen variety, as many gardeners would like to grow similar varieties in their gardens.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting