Kurnakovskoye apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Reds |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Autumn |
| Size of apples | Average |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Average tree height |
| Shelf life | Average shelf life |
| Application | Fresh , For recycling |
| Winter hardiness | High winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | Up to 5 years |


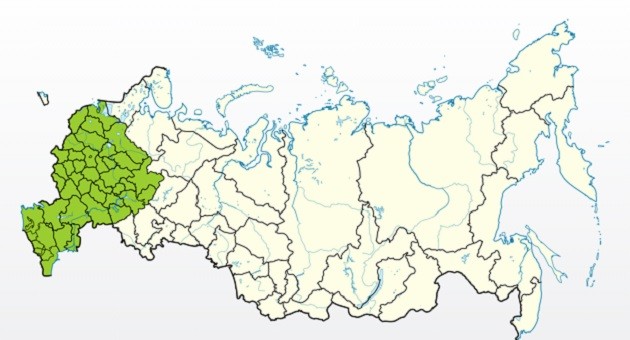 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
- Central Black Earth Region.
- Middle zone.
- Moscow region.
- North Caucasus.
- Crimea.
- Leningrad region.
- Volga region.
Origin
This apple tree was developed by the All-Russian Research Institute of Fruit Crop Breeding. In 1981, the first seedling of the new variety was obtained by crossing two hybrids: PA-29-1-1-63 and 814. Only 11 years later, in 1992, was it recognized as an elite variety and sent for official variety testing to orchards in the village of Zhilina in the Oryol Region. The authors of this new variety are Evgeny Nikolaevich Sedov, Evgeny Alekseevich Dolmatov, Zoya Mikhailovna Serova, and Vladilen Vasilyevich Zhdanov.
Kurnakovskoye proved itself to be a promising variety, so it was registered as early as 1995. However, it wasn't until 2002 that the variety was officially included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements and zoned for the Central Black Earth and Central regions. In fact, it can easily be grown throughout European Russia, in more northern and southern latitudes, in warm Crimea and the Caucasus, and even in the Urals.
Content
Description of the Kurnakovskoye variety
 These not very dense and tall apple trees immediately attracted the attention of gardeners. Despite their limited zoning, they can grow in a wide variety of regions, even quite harsh ones. The trees are highly environmentally resilient, undemanding of soil, moisture, and care, and are immune to scab due to their genetic immunity.
These not very dense and tall apple trees immediately attracted the attention of gardeners. Despite their limited zoning, they can grow in a wide variety of regions, even quite harsh ones. The trees are highly environmentally resilient, undemanding of soil, moisture, and care, and are immune to scab due to their genetic immunity.
The fruits are attractive, very tasty, and sweet. They are easy to transport, even over long distances, ripen late, and have a long shelf life. The Kurnakovskoye apple tree is recommended for intensive cultivation in commercial and industrial orchards, as well as for small garden plots.
Apples: What do they look like?
 The fruits are medium-sized, weighing 130-160 grams, and are generally uniform in size, round or round-conical, sometimes slightly flattened or, conversely, elongated. They are symmetrical or slightly slanted to one side near the stalk, with subtle ribbing, visible only near the calyx.
The fruits are medium-sized, weighing 130-160 grams, and are generally uniform in size, round or round-conical, sometimes slightly flattened or, conversely, elongated. They are symmetrical or slightly slanted to one side near the stalk, with subtle ribbing, visible only near the calyx.
The skin is smooth, glossy, fairly dense, elastic, thin but firm, and may have a light, colorless oily coating. Its base color is green, turning greenish-yellow as it ripens. Approximately 65-90% of the surface is covered by a blush, consisting of pinkish-red, crimson, or crimson-brown stripes and streaks, speckled and blurred. Subcutaneous punctures are numerous, large, gray or greenish-gray.
Experts advise assessing the chemical composition based on the following indicators:
- P-active substances (catechins) – 413 milligrams.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 10.8 milligrams.
- Fructose (total sugars) – 10.5-11.2%.
- Pectins – 12.6%.
- Titratable acids – 0.77%.
The apples have medium-firm flesh, very tender and juicy, and a fine-grained texture. It breaks easily when bitten. It's sweet and sour, leaning heavily toward sweetness, but with a distinct apple tartness. Professional tasters give the fruit at least 4.2-4.4 out of 5.
Kurnakovskoye apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 The appearance of this apple variety is not particularly striking. The trees are of medium vigor and height. They can reach a maximum height of 4-5 meters, and even then, in suitable conditions, without formative pruning.The branch density is also medium, as is the foliage. The shape is pyramidal, but over time it can become broadly oval, spreading, and even somewhat drooping. The shoots are geniculate, set at right angles to the conductor, and covered with grayish-brown bark, prone to cracking and peeling.
The appearance of this apple variety is not particularly striking. The trees are of medium vigor and height. They can reach a maximum height of 4-5 meters, and even then, in suitable conditions, without formative pruning.The branch density is also medium, as is the foliage. The shape is pyramidal, but over time it can become broadly oval, spreading, and even somewhat drooping. The shoots are geniculate, set at right angles to the conductor, and covered with grayish-brown bark, prone to cracking and peeling.
The leaves are larger than average, glossy, bright or dark green, richly colored, and coarsely ribbed. The undersides are covered with a felt-like pubescence. They are ovate, oval, elongated, and long-pointed, with tips often curled in a helical fashion. The margins are crenate, serrated, and serrated, and can fold into a boat-like shape. The root system is fibrous and branched, though only on wild specimens may it be taproot. It is well-drained and moderately to moderately adapted to water-seeking.
Productivity and pollination
The Kurnakovskoye variety is considered to be highly productive; the tree produces crops regularly and early, without resting.
A good apple grower can produce approximately 180-220 kilograms of apples per year from a fully mature tree. Under optimal growing conditions, in favorable years with suitable climate and careful care, this figure can be increased to 250-280 kilograms.
The variety is considered conditionally self-fertile, meaning it produces fruit even when there are no other apple trees nearby that are at the same time as their buds. However, to maximize yields, cross-pollination is essential. Experienced gardeners bring mobile apiaries to their orchards during the blooming period and spray the trees with syrup.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
These apple trees are considered moderately tolerant of low temperatures. In fact, they can withstand temperatures as low as -18-22°C for quite long periods, up to 2-3 weeks at a time. However, sudden temperature fluctuations and high humidity can damage the trees. Therefore, they should be adequately protected from frost during the winter.
Kurakovsky has genetic immunity to scab (Vf gene in the code). It is resistant to powdery mildew, cytosporosis, moniliosis, and other apple tree diseases. However, regular preventative spraying is still advisable. At the same time, it's important to treat for parasitic infestations, which can also negatively impact the harvest.
Rootstocks and subspecies
These apple trees are considered a relatively young variety, so there's no talk of any subspecies yet. However, they can be grown on a wide variety of rootstocks, the best of which are considered standard and semi-standard. There are no columnar Kurnakovsky rootstocks, but it's quite possible to form a creeping rootstock from it.
Features of growing Kurnakovsky
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- Before planting, it's important to choose a location where the groundwater table isn't too high. If underground streams and rivers are no deeper than 1.8-2 meters, trees will grow roots that will rot and eventually die.
- There aren't many soil requirements for this variety, but fertile soil is preferable. With proper care, regular feeding, and fertilizer, this tree will grow even in sand or clay. The main thing is that the soil isn't too acidic or salty.
- A sunny, open space exposed to all winds is the best location for an apple tree. However, it's important to keep drafts at bay. In the shade, apple trees grow weak and may refuse to bloom or bear fruit altogether, or do so much later than their peers growing under ultraviolet rays.
- It's essential to leave at least 3-3.5 meters between trees in rows. The distance between rows is usually even larger, about 4-5 meters.
- It's customary to prepare the holes well in advance, somewhere between six months and a year before planting. If you've already purchased or are planning to plant the seedlings, you can simply let the holes sit for two to three weeks. They're dug 80-95 centimeters deep and the same diameter, with fertilizer placed at the bottom, then a drainage layer added, watered, and left outdoors.
- The apple tree graft must always remain above ground to prevent roots from growing higher. Otherwise, the tree will permanently lose the qualities of the rootstock.
- Place the seedling on a mound of drainage material, cover with soil, and gently compact it to eliminate any air pockets or voids that can cause root rot. Water the seedling with 45-50 liters of water, and mulch the surface with manure, compost, sawdust, or any other material.
Landing dates
Apple trees can be planted in early spring, before the buds begin to open, around late April or early May. Make sure the soil is well warmed and there are no recurring frosts, otherwise the seedlings could be damaged.
In warmer regions, where autumns are long and frosts don't set in for a long time, and the frosts themselves aren't particularly severe, Kurnakovskoye can be planted in September or October, after the leaves have completely fallen. Trees with closed root systems can be safely transplanted into the garden at any time, even in the midst of the summer heat.
 Tree care
Tree care
Protection from frost and pests
Tree trunks don't respond well to various weather conditions, so it's best to prepare them for winter in advance. It's best to stop all watering by early autumn, in mid- to late August. Trunks should be wrapped in any kind of fabric, and young seedlings can even be covered with a tent-like covering. In particularly frosty regions, it's a good idea to sprinkle sawdust, rake hay or straw, lay spruce branches, or even a 10-15 centimeter layer of soil around the root zone. All of this should be removed in early spring.
Timely preventative measures, such as spraying with various commercially available products, are effective against insects. It's also a good idea to whitewash the trunks with lime to prevent pests from nesting in the bark crevices. However, this won't protect against rodents. To protect against them, you can coat the apple trees with lard or fuel oil.
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Twice-daily digging in spring and fall will help maintain the tree trunk area. A few additional hoes during the summer will also completely eliminate weeds and loosen and oxygenate the soil. It's a good idea to loosen the soil the day after watering, especially in hot and dry weather.
Trees don't need to be watered very often; they're perfectly capable of finding moisture in the soil themselves. A total of 4-6 waterings is sufficient, and even then, only when rainfall is low. It's a good idea to add fertilizer and other nutrients along with the water to make it much easier for the tree to absorb them.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
Kurnakovskoye has a medium density, so maintaining it is easy. Its optimal form is a sparse, tiered tree, with branches spaced at different heights. Pruning begins in the first year after planting, shortening the trunk by a third, and shortening all skeletal shoots in the tiers by an additional 5-15 centimeters.
Sanitary pruning necessarily involves removing all damaged, broken, dry, or diseased branches. At the same time, you can remove any upward-protruding or inward-growing branches that can lead to excessive tree density. The cut areas are sealed. garden pitch, or paint, drying oil or even swamp.
Pollinator varieties
- Antonovka.
- Borovinka.
- Idared.
- Korobovka.
- Titovka.
- Premiere.
- Elstar.
Reproduction
Diseases and pests
- Cytosporosis.
- Powdery mildew.
- Moniliosis.
- Black crayfish.
- Hawthorn.
- Aphid.
- Scale insect.
- Leaf roller.
Ripening and fruiting of Kurnakovsky
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
The hybrid's first fruiting didn't begin until the eighth year after being sown in the soil in a greenhouse. However, with other propagation methods, the tree begins to bloom earlier. By the second or third year, buds begin to appear, which should be picked off. These are mostly barren flowers, which will waste the apple tree's energy. Full fruiting can be expected as early as the fourth or fifth year after transplanting the seedling into open soil.
Flowering time
The buds open mid-season, like most other apple trees. Around May, fragrant, snow-white or slightly pinkish flowers bloom, large to medium-sized, in clusters of 6-8. They are very beautiful, densely covering the branches. The process lasts approximately 12-16 days, during which time bees and wind usually have time to pollinate.
Fruiting and growth
Average growth rate is approximately 25-35 centimeters per year. Growth can be much faster before fruiting begins, but then slows. After the first fruits, it will take at least 4-6 years for the harvest to reach its maximum. However, the tree's lifespan is up to 50 years or more, during which time it bears fruit almost continuously.
Apples begin to ripen as early as late September or early October. That's when it's time to start harvesting. The cooler and rainier the summer, and the colder the preceding winter, the later the apples ripen. However, they cling tightly to the branches, so they rarely fall to the ground. They can be transported long distances without any problems; they travel well. Their shelf life reaches 4-5 months; sometimes they last until spring in a special refrigerator or a suitable cellar filled with sawdust or sand.
Top dressing
- Manure.
- Compost.
- Humus.
- Superphosphate.
- Chicken manure.
- Mineral and nitrogenous complexes.
- Ammonium nitrate.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Transplant into the sun.
- Protect from drafts.
- Limit or activate watering.
- Eliminate pests.
- To stop diseases.
Why do apples fall?
- Weather phenomena.
- Early frosts.
- Pests or diseases.

Share your own experience with the Kurnakovskoye apple tree variety so that even novice gardeners have no questions about cultivating these trees.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting