Barguzin apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Reds |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Summer |
| Size of apples | Average |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Columnar tree |
| Shelf life | Low shelf life |
| Application | Fresh , For recycling |
| Winter hardiness | High winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | Up to 5 years |


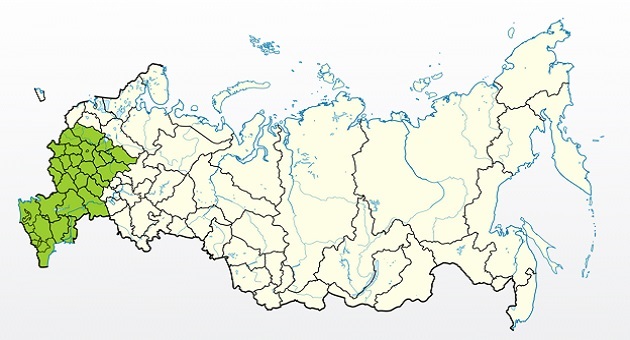 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
- North Caucasus.
- Crimea.
- Northern regions (partially).
- Moscow region.
- Middle zone.
- Leningrad region.
Origin
The variety with the beautiful name was developed at the All-Russian Research Institute for Fruit Crop Breeding (formerly VNIISPK), the oldest experimental center in our country. The variety's creators are Viktor Valeryanovich Kichina and his faithful assistant Nadezhda Morozova, who have developed dozens of diverse crops, including apple trees. The working name of the hybrid, under which it was first selected for the elite in 1976, was KV-53.
The apple tree's name was chosen deliberately; it's more than just a pretty combination of sounds. Locals around Lake Baikal use the word "Barguzin" to describe the fresh, cold, dangerous, yet essential for shipping, northwesterly wind blowing toward Olkhon Island. Its arrival typically brings bright, sunny weather, but waves near the shore can easily reach 4 meters in height..
The variety underwent extensive testing, and it was ultimately decided to use it as a rootstock. Although the apple tree is quite good and produces good yields of delicious fruit, it has not yet been entered into the State Register of Breeding Achievements and is not zoned. It can be grown in virtually any region of the central Russian region, the Central Black Earth Region, the Volga region, the southern regions, and some northern regions.
Content
Description of the Barguzin apple variety
 Compact columnar trees that take up minimal space in the garden yet consistently produce bountiful harvests are the dream of any amateur gardener, and even a professional one. Barguzin is resistant to scab and other fungal infections, tolerates long periods of cold quite well in our country's harsh climate, with proper preparation and protection, and is very beautiful and decorative.
Compact columnar trees that take up minimal space in the garden yet consistently produce bountiful harvests are the dream of any amateur gardener, and even a professional one. Barguzin is resistant to scab and other fungal infections, tolerates long periods of cold quite well in our country's harsh climate, with proper preparation and protection, and is very beautiful and decorative.
Experienced gardeners recommend this variety for small private gardens, but it is also suitable for large commercial intensive gardens with an industrial focus.
Apples: What they look like
 The fruits are generally medium-sized, barely reaching 85-140 grams in weight. They are round or round-conical, sometimes turnip-shaped, and can be slanted or asymmetrical. With good care and very favorable conditions, they can grow to 140-170 grams, but this is rare and occurs in some years. The fruits are smooth, but the ribbing near the calyx can be clearly visible.
The fruits are generally medium-sized, barely reaching 85-140 grams in weight. They are round or round-conical, sometimes turnip-shaped, and can be slanted or asymmetrical. With good care and very favorable conditions, they can grow to 140-170 grams, but this is rare and occurs in some years. The fruits are smooth, but the ribbing near the calyx can be clearly visible.
The skin is dense, fairly thick and strong, elastic, smooth, and has a natural sheen. It has a greenish tint when young, turning yellow or even golden with age. The blush is predominantly mottled, bright red, red-orange, or slightly pinkish-crimson, covering at least 45-65% of the entire surface. Subcutaneous dots are gray-green, small but fairly dense, and difficult to see on the mottled skin. The chemical composition is typically assessed based on the following data:
- P-active substances – 342 milligrams.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 10.4 grams.
- Sugar (fructose) – 13.9%.
- Titratable acids – 0.47%.
- Pectins (fiber) – 11.8%.
The flesh is medium-dense, juicy, and pleasantly textured. It can be medium- or coarse-grained, but is not at all crumbly. It usually has a beautiful greenish-cream hue, but can sometimes have a lemony hue. The flavor is considered harmonious, classified as a dessert fruit. It is sweet and sour, balanced, and pleasant, scoring 4.7 points among professional tasters.
Barguzin apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 The tree is columnar, but can develop as more than just a single trunk. Some form two or three branches that grow at a very sharp angle upward, forming a sort of narrow panicle. The trees grow from 1.5 to 2.5 and even 3 meters in height., depending on the rootstock used. The crown circumference, regardless of the training method, does not exceed 40-45 centimeters in diameter. The branches are of medium thickness, covered with light brown or greenish-brown bark, smooth, shiny, and pubescent.
The tree is columnar, but can develop as more than just a single trunk. Some form two or three branches that grow at a very sharp angle upward, forming a sort of narrow panicle. The trees grow from 1.5 to 2.5 and even 3 meters in height., depending on the rootstock used. The crown circumference, regardless of the training method, does not exceed 40-45 centimeters in diameter. The branches are of medium thickness, covered with light brown or greenish-brown bark, smooth, shiny, and pubescent.
The leaves are medium-sized and not very dense. They are dense and leathery, though not glossy, but of medium sheen, green or emerald green in color, long-pointed, with a propeller-shaped curling tip, and can be curved or folded into a boat. The leaf margins are serrate-crenate, wavy, and serrated. The root system is medium-deep, lacking a central taproot, but is most often superficial, although adapted to the search for water and nutrients.
Productivity and pollination
Barguzin is a recognized leader in productivity among columnar apple varieties.
Over the course of a season, one mature Barguzin rootstock, grown on a seed rootstock and approximately 2.2-2.5 meters tall, can yield 22-28 kilograms of delicious, aromatic apples. This is a very good yield for a columnar tree. However, with dwarf rootstocks, when trees barely reach 1.5 meters, the yield will be no more than 5-10 kilograms maximum..
The apple tree is completely self-fertile, which is considered another of its many advantages. To produce apples, there's no need for other varieties with suitable flowering times within a certain distance. However, experienced gardeners still recommend interplanting these trees, as this will result in more abundant, larger, and more abundant harvests. You can also attract insects by spraying the trees with diluted sugar or honey.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
Barguzin is quite hardy and easily tolerates temperatures down to -22-27°C with normal care and winter protection. If provided with shelter structures, even frosts of more than -30°C will be unaffected. However, caution is required; strong winds, drafts, excessive moisture, and prolonged frosts can damage the trunks and even lead to their death.
The variety exhibits a fairly good level of resistance to a wide variety of diseases: from the popular scabies, to the point of rare black crayfish and fire blight. It may not be affected even during years of severe epiphytotics, and if it is, only the foliage is affected. However, prevention should not be neglected, as the risk, although minimal, still exists.
Rootstocks and subspecies
This variety is grown on various rootstocks, which can cause slight changes in its qualities and properties. For example, trees may be taller or shorter, and the fruits larger or smaller. All information on this can be obtained from the seller or nursery owner. No distinct subspecies of Barguzin exist yet, and it's likely they never will.
Features of growing Barguzin
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- All fruit trees prefer open areas where their crowns receive ample sunlight, and these apple trees are no exception. In the shade, they will grow thin and weak, and if they do produce fruit, it will be small, sour fruits.
- It's best to protect the garden from drafts, which often lead to diseases. However, crown ventilation is essential, as it increases the risk of disease.
- Plants tolerate high groundwater levels (up to 1.5-1.7 meters). However, if the groundwater level is higher, careful drainage will be required or the planting should be avoided altogether. Barguzin is not typically planted near lakes and rivers, streams and shallow wells, springs, and ponds.
- The compact crown allows trees to be spaced 0.5 meters apart within a row, but a 1-meter gap between rows is recommended. This will make tending the trunks and harvesting easier.
- Preparing the holes for planting the variety in advance is possible, but not necessary; allowing them to sit outdoors for two to three weeks is sufficient. The holes should be at least 80-90 centimeters in diameter and 60-70 centimeters deep. Add a small amount of fertilizer to the bottom, cover with drainage material, and then fill with water (35-40 liters).
- If the goal is to preserve the properties of the rootstock, then the root collar of the seedling must be left above the surface by at least 5-7 centimeters.
- Stake stakes are dug into the holes immediately on the north side for support. They can be made of plastic, wood, or even metal. If it's possible to create a kind of hedge across the entire row, it will be much easier to cover the apple trees with a canopy in the future.
- Place the tree in the hole, hold it upright, cover with soil, and compact it by hand. Add 30-45 liters of water to the surface, then apply mulch to retain the water.
Landing dates
The Barguzin variety thrives when planted both in early spring (March-April) and late fall (September-October). However, experts say that in the south and in mild climates, it's better to plant trees before the onset of cold weather, and in harsh climates, afterward. This allows them to adapt much better to the new conditions. Trees with closed root systems can be transplanted into open soil at any point during the growing season.
 Tree care
Tree care
Protection from frost and pests
Young trees should be covered with special care for the winter, but even as they mature, they also need protection. It's common to throw bundles of straw or hay, spruce branches, or even rake 15-20 centimeters of soil over the roots. All this will need to be removed in the spring, otherwise the trees will become diseased. In harsh climates, it's best to cover the Barguzin tree with a tent-like covering using tarpaulin or film; agrofibre or polyethylene will also do.
To discourage insects from overwintering in the cracks of the bark or near the rhizomes, the trunks are whitewashed with a thick lime solution using a regular brush. Rabbits, hares, hamsters, and mice that eat the bark can be repelled by smearing the tree with melted animal fat or grease.
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Dig the soil around the trunk twice a year: in early spring, before the buds begin to open, and in late fall, after the leaves have fallen. This must be done very carefully to avoid damaging the shallow root shoots. As the tree grows, you can hoe the soil, removing any weeds or root suckers. It's best to do this the day after watering, so the soil around the rhizome doesn't become compacted to a granite consistency.
Trees need to be watered thoroughly, but not excessively. A drip irrigation system or regular sprinkler irrigation, ideally computer-controlled, is ideal. However, not everyone has this capability, so simply watering once a week or ten days during hot weather can be effective. If it rains, start counting down the required time from there, and continue this way until autumn.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
Properly pruning a Barguzin can be tricky. To simplify the task as much as possible, all lateral skeletal shoots are cut off, leaving a single trunk. However, this isn't always possible. Alternatively, two or three shoots are formed, growing as vertically as possible, and then removed one by one, leaving the most fruit-bearing ones.
Dry branches should be regularly pruned, as they will drain the tree's energy and unnecessarily thicken its crown. However, the variety requires no rejuvenation, as its lifespan is already short, only 15-25 years, depending on care, weather, and climate.
Pollinator varieties
- Jonathan.
- Korobovka.
- Vazhak.
- Chervonets.
- Triumph.
- Ostankino.
- Borovinka.
- Iksha.
Reproduction
- Rooting.
- Kidney grafting.
- Growing from seeds.
- Cuttings.
Diseases and pests
- Black crayfish.
- Powdery mildew.
- Bacterial burn.
- Scab.
- Green aphid.
- Codling moth.
- Leaf roller.
- Hawthorn.
Ripening and fruiting of Barguzin
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
This is a very early-bearing variety, producing its first flowers in its first year, even if grown in a nursery. Experts advise plucking every last bud immediately to allow the apple tree to develop a root system and foliage, as well as thicken the trunk and shoots. The first harvest can only be collected in the third or fourth year. This yield can amount to at least 5-8 kilograms of fragrant, delicious, and juicy apples.
Flowering time
This is a late-summer apple tree, so its blooming season can be safely considered mid-season. It begins to open buds around mid-May, but rain, cold, or other "cataclysms" can delay this until the very end of the month. However, by the 10th or 12th of the first month of summer, it will definitely have finished blooming and fruit buds will be visible.
Barguzin's flowers are large, often pink or at least slightly pinkish. They are cup-shaped and have large, fleshy petals, gathered in clusters of 6-8. They are very beautiful and fragrant, densely covering the tree's branches, interspersed with small, light green leaves, creating a very attractive appearance.
Fruiting and growth
The tree is fast-growing, capable of growing about 50-70 centimeters per year, reaching its full height in just a couple of years. Barguzin also increases its fruiting rate, and by the age of 5-7 years, a significant amount of fruit can be harvested. The branches are literally shed, so the tree often requires additional pruning. support until they are fully ripe and harvested.
The fruits ripen in the second half of August, often at the very end of the month, leading many to mistakenly consider them autumn fruits. They can fall to the ground, so it's best to harvest them promptly. The fruits are stored in wooden crates, sprinkled with sand or sawdust. The fruits are easy to transport and don't suffer much during transit, but their shelf life is limited, only 45-60 days, after which they must be fully processed.
Top dressing
- Peat.
- Compost.
- Ammonium nitrate.
- Humus.
- Superphosphate.
- Manure.
- Mineral complexes.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Check for pests or diseases.
- Transplant into the sun.
- Water.
- Fertilize.
Why do apples fall?
- Wind, hail, hurricane, rain.
- Pest damage.
- Diseases.

Please leave your feedback on the Barguzin variety, as many gardeners would like to grow similar varieties in their gardens.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting