Kutuzovets apple tree: characteristics of the variety and care
| Color | Greens |
|---|---|
| Ripening season | Autumn |
| Size of apples | Average |
| Taste | Sweet and sour |
| Crown type | Average tree height |
| Shelf life | High shelf life |
| Application | Universal variety |
| Winter hardiness | Average winter hardiness |
| Fruiting age | From 5 years old |


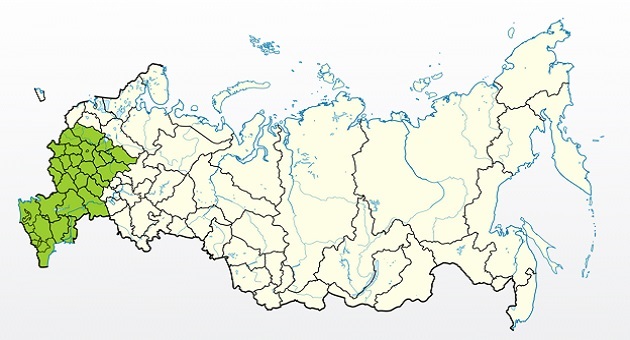 History of origin and regions of growth
History of origin and regions of growth
Growing regions
- Middle zone.
- Crimea.
- North Caucasus.
- Some northern regions.
Origin
In 1935, hybridization was conducted at the Zhigulevskie Sady Research Institute of Horticulture and Medicinal Plants in Samara, producing a new late-winter ripening seedling. The famous Skrizhapel and Ranet Simirenko were used as parents. The crossing was conducted under the guidance of the renowned plant breeder S.P. Kudrin, and by 1947, the resulting material had already produced good, unusual fruits.
During the war, testing was suspended but soon resumed. Nevertheless, it took more than three decades for the new variety, named Kutuzovsky, to gain recognition. In 1979, it was classified as an elite variety, included in the State Register, and zoned for the Middle Volga region. In fact, it can be grown in mild and temperate climates, and even in some more northern regions.
Content
Description of the Kutuzovets apple variety
 These relatively frost-resistant, late-winter-ripening apple trees are sure to attract the attention of gardeners, both professional and amateur. They are relatively easy to grow and hardy, produce high yields, and are very compact, significantly reducing the space they take up in the garden and significantly simplifying their maintenance.
These relatively frost-resistant, late-winter-ripening apple trees are sure to attract the attention of gardeners, both professional and amateur. They are relatively easy to grow and hardy, produce high yields, and are very compact, significantly reducing the space they take up in the garden and significantly simplifying their maintenance.
The fruits have high consumer and commercial qualities and can retain their quality for a long time during storage. They are recommended for commercial cultivation in intensive gardens and small private plots.
Apples: What they look like
 The fruits are mostly medium or slightly larger than average in size, weighing approximately 110-160 grams. They are round or round-flattened, smooth, and generally uniform in size, symmetrical, with ribbing barely visible to the naked eye.
The fruits are mostly medium or slightly larger than average in size, weighing approximately 110-160 grams. They are round or round-flattened, smooth, and generally uniform in size, symmetrical, with ribbing barely visible to the naked eye.
The skin is dense, glossy, shiny, tender, not rough, and has a light waxy coating. It is green, turning greenish-yellow or lemon-colored as it ripens. The blush is pale, vaguely streaked, a dull pinkish-red, barely noticeable on the surface, and covers only the side of the apple that receives the most sunlight. Subcutaneous punctures are large, evenly spaced, light gray or slightly greenish, and clearly visible on the skin. Chemical properties are best characterized by the following data per 100 grams:
- P-active substances (catechins) – 185 milligrams.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 2 milligrams.
- Total sugars (fructose) – 10.1%.
- Pectins (fiber) – 6.3%.
- Titratable acids – 0.42%.
The fruit's flesh is dense, fine-grained, and can be slightly crunchy, with a pleasant texture and tenderness when ripe for consumption. It is white or slightly greenish, with a distinct aroma, but is usually excessively firm immediately after picking. The flavor is sweet and sour with pronounced spicy notes. According to professional tasters, it scores 4.5 and 4.4 points out of 5 for appearance and flavor.
Kutuzovets apple tree: characteristics
Crown and root system
 The trees are considered to be of medium height, although it is more logical to classify them as natural dwarfs, since They reach a maximum height of 3-3.5 metersHowever, most owners perform formative pruning, keeping the trunks below 2-3 meters. This makes them much easier to care for and harvest. The crown is round or broadly oval, and over the years, it can become not only spreading but even weeping. The shoots extend from the trunk at an angle close to right angles, and fruiting is primarily concentrated on the spurs and fruiting branches.
The trees are considered to be of medium height, although it is more logical to classify them as natural dwarfs, since They reach a maximum height of 3-3.5 metersHowever, most owners perform formative pruning, keeping the trunks below 2-3 meters. This makes them much easier to care for and harvest. The crown is round or broadly oval, and over the years, it can become not only spreading but even weeping. The shoots extend from the trunk at an angle close to right angles, and fruiting is primarily concentrated on the spurs and fruiting branches.
The branches are medium-thick, covered with greenish-brown or simply brown bark, and lightly pubescent. The leaves are dense, medium-sized, rounded-elongated, long-pointed, leathery, dark green or emerald. They have finely toothed, serrated, wavy margins, and sometimes fold into a boat-like shape. The root system is medium-deep, can be superficial, branched, and well adapted to water-seeking, with or without a central taproot, depending on the rootstock used.
Productivity and pollination
The tree is considered a high-yielding variety, although it can't compare to the most advanced ones. However, it takes up relatively little space on a plot, so its overall yield per hectare is pleasantly surprising (115-120 centners).
One mature tree of the Kutuzovets variety can produce approximately 55-75 kilograms of tasty and aromatic fruits per season..
The variety is considered conditionally self-fertile, meaning that without other apple trees nearby suitable for cross-pollination, the yield will be limited, no more than 10-15% of the maximum possible yield. Therefore, it's common to interplant them to achieve good results. You can also spray the trees with sugar diluted in water during flowering, which will attract more bees to the plantings.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
Kutuzovets's frost resistance is questionable, so it's always worth considering carefully before purchasing seedlings. They grow well in temperate continental climates or the mild conditions of Crimea, the North Caucasus, and the Volga region, but in more northern, harsh conditions, they require careful winter protection. Frosts of -17-20°C lasting more than 2-3 weeks can kill entire plantings if measures are not taken correctly.
The variety has a moderate resistance to scab and powdery mildew. They are relatively resistant to them, and with proper care, they can be prevented entirely. They are extremely rarely affected by fruit rot or pitted bitterness, but these insects readily damage not only foliage and fruit, but also the wood.
Rootstocks and subspecies
| Subspecies | Description |
| Half-dwarf | To cultivate this subspecies, a seedling of the Anis variety is most often used. This type of tree produces even more compact trees, while also becoming more winter-hardy. Otherwise, the trees retain virtually all the qualities of the parent variety. |
| Winter | This version of Kutuzovets is considered suitable even for growing in much harsher conditions than the central zone of our country, for example, UralsOptimally, it is grafted onto a dwarf vegetative rootstock (OKS). The fruits will be somewhat smaller, but their quality will not be affected. |
Features of growing Kutuzovets
 Landing
Landing
Basic conditions
- The planting site must be chosen very carefully. It should be an open, sunny space, but preferably free of drafts, and ideally completely sheltered from the wind. For example, building walls, taller trees, fences, and hedges can help protect against drafts.
- It's best to have groundwater at a depth of 2-2.5 meters or deeper. Otherwise, the trees' roots may reach the groundwater and rot. Therefore, planting Kutuzovets near ponds, springs, rivers, or lakes is also not a good idea.
- It wouldn't hurt to leave a distance of up to 4 meters between trees and up to 5 meters between rows. This will prevent them from interfering with each other's roots or branches in the future.
- It's best to prepare the holes in advance, as experienced gardeners do, in the fall or spring. However, if you haven't done so yet, 3-5 weeks will be sufficient. Dig holes 70-90 centimeters deep and up to 1 meter in diameter, fill the bottom with soil and fertilizer, place stones or broken bricks on top, and then fill the entire thing with water (35-40 liters).
- It's best to immediately dig stakes into the holes to tie the seedlings to. These can be made of wood, metal, or plastic. Ideally, they should be positioned on the north side of the tree trunk.
- The root collar should always be left above the surface; 8-12 centimeters is ideal. Otherwise, the seedlings will root above it, completely negating all the properties of the rootstock.
- The seedling is placed in a hole, covered with soil, compacted, watered with 15-25 liters of water, and the surface is mulched.
Landing dates
This variety can be planted in either spring or fall; survival rates are virtually identical in both cases. The only consideration is the region. In the mild southern climate, planting time is unimportant, but in harsher conditions, spring planting is best to ensure the young trees survive and are well-established by winter.
Protection from frost and rodents
The delicate tree requires careful protection from frost, which is why various measures are taken. Mats of dry grass or straw bales are placed on the root zone near the trunk, and the soil is raked up to a depth of 20-30 centimeters, which is then removed in the spring. The trunks are wrapped in burlap or other materials, and, if possible, the apple trees are covered with a tent-like covering.
Standard insect control measures are sufficient: whitewashing the tree to a height of 1-1.4 meters with lime. This will prevent them from settling in bark crevices and around the rhizomes. To prevent rodents from eating young bark, you can coat it with grease or lard.
 Tree care
Tree care
Loosening the soil, watering: proper agricultural technology
Once a year, carefully dig up the root zone to avoid damaging the shallow roots. At the same time, remove weeds, other plants, and root suckers. You can hoe the soil more frequently, but don't overdo it.
Trees of this variety require a specific watering schedule, and it should be infrequent. The first application should be before the buds begin to open, followed by another watering 25-30 days after flowering, and then two weeks before harvest. Some recommend watering again in late autumn, around October, but it's best to monitor the weather; if frost is forecast, it's best to avoid this idea.
Pruning: simple crown shaping
Shaping the tree won't take much time and won't require much effort or expertise, as the crown isn't particularly prone to becoming dense. In the first year, the central trunk is shortened by a third, and only 2-4 main branches are left, spaced far apart and at different heights. In the future, all that remains is to maintain the same shape, trimming off shoots that sprout upward and those that grow inward.
Sanitary pruning can be done at any time, removing diseased, damaged, or dried shoots. All cut areas should be immediately sealed with water-based paint, garden varnish, or even just a bolt. This will help the tree cope with stress more easily.
Pollinator varieties
Reproduction
- Rooting cuttings.
- Grafting by buds and cuttings.
- Growing from seeds.
- Clones (layering).
Diseases and pests
- Powdery mildew.
- Cytosporosis.
- Fruit rot.
- Scab.
- Cytosporosis.
- Tinder fungus.
- Green aphid.
- Codling moth.
Ripening and fruiting of Kutuzovets
 The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting
This variety isn't particularly early-bearing, although it may produce a few inflorescences in the 4th to 6th year, which are best picked. The first fruits are harvested in the 6th to 8th year, when it's possible to harvest approximately 5-15 kilograms of fruit from the tree for sampling.
Flowering time
In warmer regions, apple trees typically bloom around the second or third week of May, like most winter varieties. However, the timing can vary significantly depending on climate and weather. In some cases, blooming can extend until early June, lasting approximately 10-14 days. The flowers themselves are large, delicately white and pink, fragrant, and borne in small clusters.
Fruiting and growth
The tree gains height quite quickly, averaging 25-45 centimeters per season. Therefore, it reaches its maximum height before reaching ten years of age. Fruiting also increases quite quickly after the tree begins. By the 9th or 10th year, a maximum harvest of 60-70 kilograms can be achieved, and sometimes even more. Harvests largely depend not only on the weather but also on feeding and care. Fruiting is usually not periodic, but occasionally the apple tree may give itself a rest.
The fruit can be harvested as early as late September; they will keep well in a cellar or refrigerator. However, eating them raw right away isn't the best idea, as their technical ripeness doesn't coincide with their consumer maturity. If you can't harvest the fruit in mid- or late October, it's best to let them rest in a cellar for 30-45 days before eating them. The apples don't fall off the branches and can be stored until spring or even summer, practically until the next harvest.
Top dressing
- Compost.
- Humus.
- Nitrogen fertilizers.
- Ammonium nitrate.
- Mineral complexes.
- Superphosphate.
- Manure.
What to do if it doesn't bloom or bear fruit
- Check for pests and diseases.
- Transplant.
- Limit watering.
Why do apples fall?
- Natural factors.
- Pests.
- Diseases.

Leave your feedback on the unusual Kutuzovets variety to share your experience with other professional and amateur gardeners.

 Landing
Landing Tree care
Tree care The beginning of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting