
How to plant an apple tree if the groundwater is close: important rules for a good harvest
Even though they recognize that a high groundwater level relative to the site's surface is a contraindication to planting an apple orchard in such an unsuitable location, some gardeners simply have no choice. If you're unlucky enough to be located in a flood-prone area, be sure to familiarize yourself with all the nuances of planting trees in such conditions.
Content
- How to determine high water levels
- The influence of groundwater
- Apple tree varieties that are not afraid of groundwater
- Planting apple trees near groundwater
- Planting in spring and autumn
- Dwarf apple trees
- Columnar apple trees
- Drainage for water drainage
- Features of further care
- Peculiarities of planting apple trees in different types of soil
- How to save an apple tree if its roots have reached the groundwater
- Conclusion
How to determine high water levels
 Apple trees do not tolerate excess moisture in the soil very well. When the tree's roots reach the waterlogged soil, they begin to rot, and the crown withers and falls off. To avoid damaging the seedlings and wasting time, it's important to survey the area before planting and determine the depth of any problem areas. Observe the following:
Apple trees do not tolerate excess moisture in the soil very well. When the tree's roots reach the waterlogged soil, they begin to rot, and the crown withers and falls off. To avoid damaging the seedlings and wasting time, it's important to survey the area before planting and determine the depth of any problem areas. Observe the following:
- how high the water level is during a flood, autumn rains or a rapid and voluminous downpour;
- how quickly it decreases.
Keep in mind that groundwater can be stagnant or flowing. Moving water won't harm stone fruit crops, even if it's located quite high.
Pay attention to the weeds growing in the area. Where the soil is more flooded than usual, sedge and coltsfoot thrive.
To determine how deep the water-saturated layer goes, do the following:
- In the summer, when there is no rain, drill 2 control wells up to 1.5 m deep in opposite areas of the future garden.
- After 24 hours, measure the amount of liquid that has appeared in them. Count from the soil surface to the water's edge.
- Monitor the wells for two months. If the water level is 1 meter or higher, there's no point in planting a garden there. Drainage would be too labor-intensive and costly.
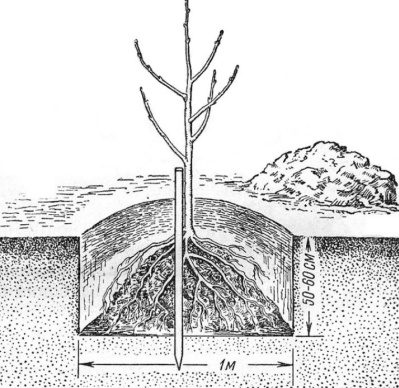
 A distance of 5–6 m from the surface, but no less than 1.7–2.5 m, is considered the absolute norm. Stone fruit crops thrive in areas where the groundwater level does not exceed 2 m. After surveying the area, a decision is made on the feasibility of planting stone fruit crops.
A distance of 5–6 m from the surface, but no less than 1.7–2.5 m, is considered the absolute norm. Stone fruit crops thrive in areas where the groundwater level does not exceed 2 m. After surveying the area, a decision is made on the feasibility of planting stone fruit crops.
The influence of groundwater
Apple trees' fibrous roots are strong and resilient. They typically extend to great depths. Therefore, if the groundwater level is high enough, this can lead to root rot and the death of the tree. Several additional factors can also exacerbate the situation:
- low temperature leading to hypothermia of the roots;
- poor survival of beneficial microorganisms in humid environments;
- faster frostbite in lowlands;
- lack of air circulation and oxygen starvation.
The mineral content of the soil also influences the development of stone fruit crops. High salinity levels will make the root zone unsuitable for apple trees.
Varieties apple trees that are not afraid of groundwater
 The determining factors when choosing a variety are:
The determining factors when choosing a variety are:
- type of soil and its condition;
- depth of groundwater;
- required rootstock.
Choose a variety that is grown in your region and adapted to typical climate conditions.
Of the summer varieties, the following are best suited:
- Golden Antonovka;
- White filling;
- Moscow pear;
- Dessert;
- June;
- Orlinka;
- Suislepskoe;
- Chernenko;
- Wonderful.
Varieties bearing fruit in September-October:
- Scarlet anise;
- Seedless Michurinskaya;
- Borovinka;
- Lingonberry;
- Zhigulevskoe;
- Orlovskoe striped;
- Streifling.
And finally, the winter ones:
- Grandma's;
- Belarusian raspberry;
- Orlik;
- Moscow winter;
- Russian woman;
- Dark-skinned;
- Spartan;
- Welsey.
Planting apple trees near groundwater
 When planting trees in such conditions, certain additional work must be performed. Furthermore, the method for performing the procedure must be chosen.
When planting trees in such conditions, certain additional work must be performed. Furthermore, the method for performing the procedure must be chosen.
Pillow
 This method involves creating a concrete pit, 80 cm deep and 1 m in diameter. After the mortar has hardened, the following steps are performed:
This method involves creating a concrete pit, 80 cm deep and 1 m in diameter. After the mortar has hardened, the following steps are performed:
- A layer of soil mixed with a mineral complex is poured in.
- The planting material is installed and, after straightening out the root system, it is covered with soil.
- The soil around the trunk is compacted slightly and watered.
The secret of the method is that the roots that encounter an obstacle will grow almost horizontally and will not reach the groundwater layer.
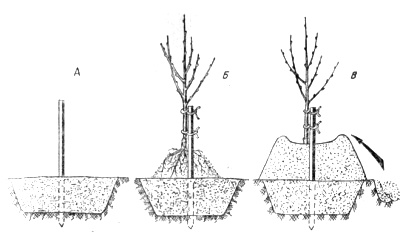
On the hill
 The future planting mound is formed from peat, mineral fertilizers and humusTo do this, they are piled together and dug up. Then, a mound 60 cm high and 1 m in diameter is formed. A stake is driven into its top and the planting material is installed, the root system of which is covered with previously collected soil. The mound is compacted and watered into small holes around the trunk. More soil is added as it settles.
The future planting mound is formed from peat, mineral fertilizers and humusTo do this, they are piled together and dug up. Then, a mound 60 cm high and 1 m in diameter is formed. A stake is driven into its top and the planting material is installed, the root system of which is covered with previously collected soil. The mound is compacted and watered into small holes around the trunk. More soil is added as it settles.
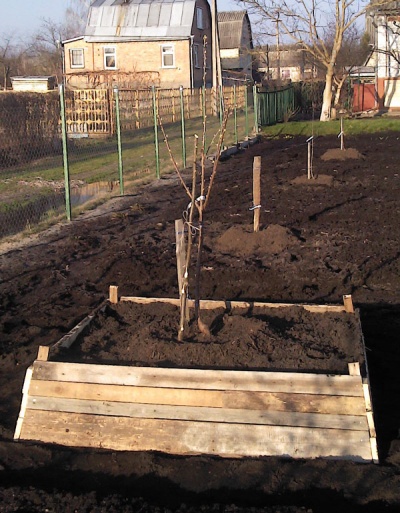
Box
 If the groundwater level prevents planting a tree using the traditional method, a protective tree box can be constructed. Its dimensions are 1 by 1.5 meters. It is filled with soil mixed with organic and mineral fertilizers. A hole is dug inside, and the young tree is planted in the hole as usual. The box is then covered with soil, periodically refreshing the mound.
If the groundwater level prevents planting a tree using the traditional method, a protective tree box can be constructed. Its dimensions are 1 by 1.5 meters. It is filled with soil mixed with organic and mineral fertilizers. A hole is dug inside, and the young tree is planted in the hole as usual. The box is then covered with soil, periodically refreshing the mound.

Planting in spring and autumn
In spring, this agricultural procedure should be carried out before the flower buds open. Hole preparation begins in the fall. For planting scheduled after the summer season, the procedure is carried out only after the leaves have fallen. In this case, the hole is prepared 2-3 weeks before transplanting the seedling to its permanent location. Gardeners determine the exact planting time themselves, as conditions vary even among neighboring plots. The key factors in this procedure are soil and weather conditions.
In this case, follow the general rules of planting:
- Do not allow the roots to dry out; plant quickly.
- Before transplanting into open ground, dip the seedling shoots into a clay slurry.
- Spread the roots over the planting hole or hill.
- Fill the hole with loose soil, not compacted clods.
- Avoid air pockets between the roots, compact the soil.
- Build watering holes.
- Add 2-3 buckets under each seedling.
- Mulch the root circle.
- Insert a stake and secure the planting material.
In the fall, plant apple trees 25–30 days before the expected frost.
Dwarf apple trees
The advantages of dwarf apple trees over tall and medium-sized ones in areas with a high groundwater level are obvious. These include:
- earlier start of fruiting (in 3–4 years);
- the ability to plant more due to their compact size;
- great reaction to top dressing and watering due to the characteristics of the root system;
- ease of pruning and harvesting.
The disadvantages of dwarf apple trees include their short lifespan and more complex preparation for winter.
Columnar apple trees
They have a shallow root system, making them ideal for gardens located in areas with excessively wet soil. They are very easy to care for. Gardeners only need to regularly prune side shoots after winter, fertilize the trees, and protect them from insects and diseases. The only drawback of columnar apple trees is their short lifespan, which typically lasts no more than 15 years. However, their high planting density and large fruit size make them ideal for planting in such areas.
Drainage for water drainage
 Installing a site drainage system can be an ideal solution for moisture-rich soils.
Installing a site drainage system can be an ideal solution for moisture-rich soils.
The removal of liquid from the seats is carried out as follows:
- Dig a hole for planting. It should be slightly smaller than the diameter of the future planting mound.
- The depth into the soil for dwarf rootstocks should be approximately 1.0–1.2 m, for medium- and tall ones – at least 1.5 m.
- Drainage is constructed (a 10–15 cm layer of crushed stone, coarse sand, fertile soil and planting soil).
A simplified drainage system involves digging canals up to 1.5 meters deep throughout the entire site. A deep well is created at the lowest point to collect water from the site.
Features of further care
After planting, apple tree seedlings will always require proper care, which includes timely fertilizing and full watering, crown formation, treatment against pests and infections, as well as loosening and mulching soil.
Fertilizers
 During the first year of a seedling's life, the fertilizer applied during planting will be sufficient. In the spring, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are recommended, and in the summer, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers. In the fall, organic fertilizers should be applied during tillage.
During the first year of a seedling's life, the fertilizer applied during planting will be sufficient. In the spring, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are recommended, and in the summer, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers. In the fall, organic fertilizers should be applied during tillage.
Trimming
 On water-saturated soils, this procedure is carried out in the spring before bud break, and in the summer, only green shoots are pinched. In the fall, after the leaves have fallen, a full pruning of the trees is carried out.
On water-saturated soils, this procedure is carried out in the spring before bud break, and in the summer, only green shoots are pinched. In the fall, after the leaves have fallen, a full pruning of the trees is carried out.
The crown of a young tree is formed until it reaches 5–7 years of age. It is necessary to carry out this annually. sanitary pruning, which consists of removing dry and diseased branches.
Watering
 In spring, the tree is watered before flowering, in summer – after fruit set, and also during the ripening period. In late autumn, a moisture-replenishing watering is essential. Afterwards, the soil around the trunk should be watered. glaze It needs to be loosened and mulched.
In spring, the tree is watered before flowering, in summer – after fruit set, and also during the ripening period. In late autumn, a moisture-replenishing watering is essential. Afterwards, the soil around the trunk should be watered. glaze It needs to be loosened and mulched.
Peculiarities of planting apple trees in different types of soil
 Clay and loamy soils typically lack ash and humus. Dig the soil to a depth of 40 cm, adding sand, lime, and superphosphate. Don't forget to plant green manure (mustard, phacelia, or lupine) and incorporate them into the soil.
Clay and loamy soils typically lack ash and humus. Dig the soil to a depth of 40 cm, adding sand, lime, and superphosphate. Don't forget to plant green manure (mustard, phacelia, or lupine) and incorporate them into the soil.
Sandy soil is characterized by a lack of nutrients, looseness, and rapid water loss. Therefore, before planting apple trees, it will require deep plowing with the addition of organic matter, lime, clay, and superphosphate.
Peat soil lacks potassium and copper, but has too much nitrogen and is highly acidic. Drain the soil and add lime, sand, and organic matter. Be sure to dig to a depth of 25 cm.
How to save an apple tree if its roots have reached the groundwater
Don't rush to cut down an apple tree if it's starting to wither due to contact with groundwater. Try draining the area using a drainage system. At the same time, lighten the crown by pruning the main tree and all scaffold branches larger than 1.5 cm in diameter. This will relieve the strain on the root system.
Try re-grafting the apple tree.
Conclusion
Experience growing apple trees in areas with high groundwater levels proves that this procedure is entirely feasible. Strictly follow the planting and care guidelines, assess the situation carefully, and select the appropriate variety.







